How to Become a Product Manager Without Any Experience

If you are inspired to become a product manager, then you should try every opportunity to learn and take on this new role for you with confidence and shining eyes.
Product managers are professionals who work with products from idea to its execution. They play a key role in small companies and startups and large corporations, being responsible for both the development and marketing of products.
Actually, there are statistics showing that today product managers can earn more than developers can. So, do not hesitate: you are making the right choice!
What does it take to become an advanced PM?
It’s unlikely, that as a child you dreamed of being a product manager. Moreover, there is no product management discipline as a real career option in a high school education system.
You may not have enough knowledge and essential product management skills at the very start of your career. It doesn’t really matter. The reason you want to turn to the product management world can be different:
- you’re a marketing person who wants to get closer to the product
- you’re a developer who wants to discover your collaborative, communicative, organizational, and marketing skills.
- you’re a thirty-year-old professional, tired of your daily routine, so you just want to turn your career path in a completely different direction.
… and so on and so forth.
Companies’ leaders and HR managers hiring new product managers today pay attention to three aspects:
- professional competencies and skills
- personal and interpersonal skills
- company fit

Personal and interpersonal characteristics is a common topic. We have recently described it in detail in our article about product managers’ skills. Company fit is a very individual aspect that depends on the specific company.
So let’s take a closer look at the professional competencies of a product manager and explore some secrets about how to become a product manager with no experience.
Professional competencies and skills
Most of the core competencies every product manager must have can be acquired in classrooms. Many professional skills develop with experience, good role models, and mentoring.
Here’re some examples of must-have professional competencies for young talents who are dreaming about how to become a product manager:
- skipping mistakes in determining product strategy at the start
- arranging customer interviews
- user testing
- running design sprints
- product feature prioritization and planning roadmaps
- resource allocation
- product positioning
- pricing
- defining and tracking appropriate metrics
- performing market assessments
Usually, product managers hone these skills over years of defining, shipping, and iterating on products.
How product managers differ in startups and mature companies?
Startups
Product managers in startups are responsible for discovery and definition issues, pricing, support, marketing, and sales.
It is crucial here to be always ready for frequent changes in direction as the company works towards product-market fit and learns to operate at scale.
- Advantages: product managers in startups can be more involved in the company strategy. They are able to make a bigger impact and to take more risks. PMs in small companies have enough influence and authority.
- Disadvantages: Startups usually do not mean any mentorship, great practices or role models. You’ll not have huge budgets to succeed at some of the things they’re tasked to do.
Mature companies
Here product managers may have a narrower scope and have some coworkers to delegate. PMs in big companies are likely to be part of a big team of managers.
- Advantages: big companies will probably provide product managers with mentoring, best company’s practices and role models. You’ll have an established customer base to work not from scratch.
- Disadvantages: product managers in mature companies have less exposure to the global strategy. They can be lost in the organizational system and policy.
Many PM newcomers learn the role but then unluckily struggle to put their knowledge into action. So, what are the ways for new product managers to become real leaders and gain stakeholders’ confidence?
10 Essential Tips for New Product Managers With No Experience

Do as much research as you can
This is the first strategic step that you must take before the first interview on the way of becoming a product manager. The detailed study of the industry, the product, its history, competitors and the target audience, will help you easily deal with the interview questions for product managers.
The more you study the product at the very beginning, the easier it will be for you to overcome the stages of the product manager career path afterward.
Try the product
If you want to understand or do something at a high level, do it yourself. It’s a crucial point for managers, working for consumer product companies, to know everything about the product they propose. You should use the product on a daily basis and be ready to try all updates first.
If you work with B2B or B2C products, ask a responsible engineer to give you access to a demo. Usually, sales managers and support guys have access to demo and staging areas.
Know your future boss’ goals
It does not require accepting the life philosophy of your boss. No one likes copycats. However, it can be important to understand his/her attitude and global product goals from his/her side.
Talk to customers
Do not doubt to communicate directly with your customers if you really strive to understand how to become a product manager. Sometimes friendly customers who use the product for a long time will want to let you in their worries, complains, or will provide you with the other feedback. This insight will help you to understand the product better and to think about your future roadmap stages.
It’s better to communicate regularly with your customers to really understand your product’s value.
Friend sales managers
It’s better to start a friendship with all team members because everyone will help you and teach if necessary. You’ll definitely cooperate with QAs and developers. However, sales managers constantly communicate with customers and know the market landscape better. They are real technical experts in the product.
Sales will show you how active customers use the product in their day-to-day lives. This experience will give you a deep insight of the product; will demonstrate all its strengths and weaknesses.
Try yourself in support
Spend a few days or even the week, answering customers’ calls and emails and solving their complicated issues. Let it be 30, 50 or even 100+ specific appeals from the clients, with which you’ll try to cope on your own.
Understand how customer support engages with customers and uses these skills to further insight into the product and customers.

Know your competitors
Before going to an interview with the company’s leaders, be sure to track the current state of two or three competitors. Look at the latest updates that were released by them and which features distinguish them from the product you are going to work with. This will add expertise and self-awareness to your current state.
Schedule professional conferences and events to attend
In the first months of working with the product, you certainly will not have time for external events. But when things get better, start searching for useful activities that will provide you with new professional knowledge and new contacts.
Read useful books for product managers
Nothing will teach you better than your own experience for sure. Only your own ideas, mistakes, and achievements will give you confidence in working with the new product. However, often the experience and theory can lead to brilliant solutions. This can be found in the books for product managers. Such a list of books with short reviews is described in our article.
Choose professional tools
As the new product manager, you’ll definitely need a friendly service with toolsets for managing your objectives and tasks. Hygger.io is right for this goal.
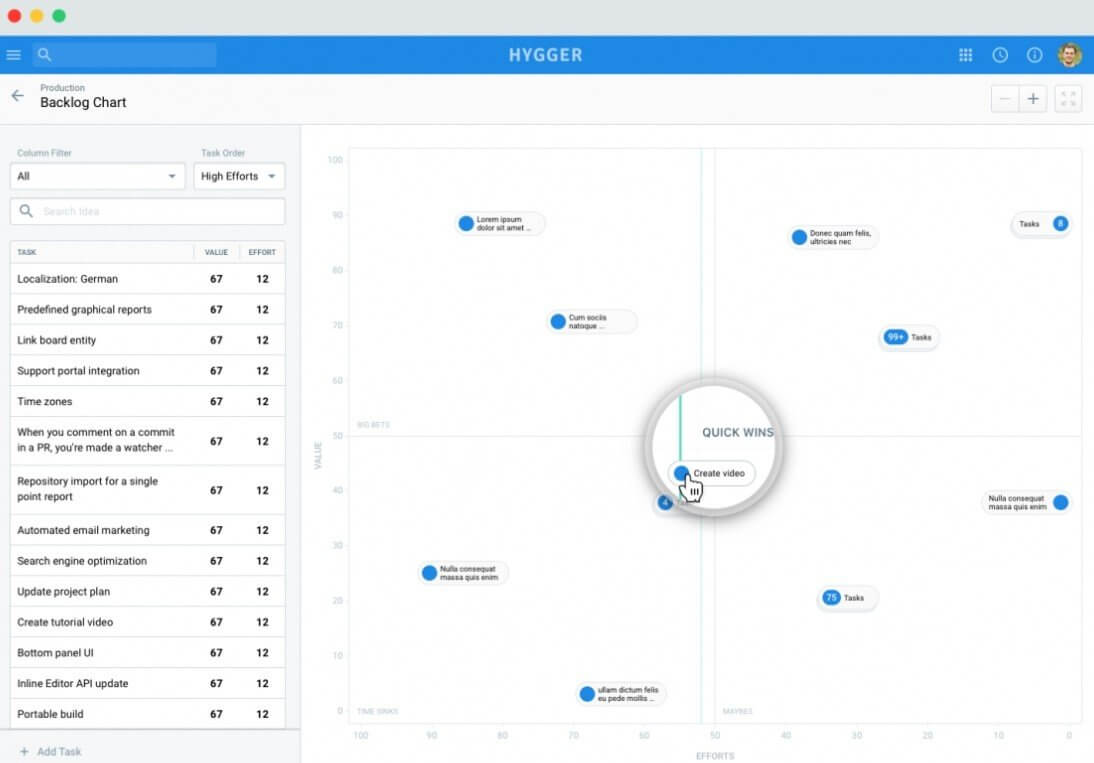
Product managers appreciate Hygger Roadmap that can be shared with all team members. Using this platform, you can also maintain a Product Backlog – storage for ideas, customers’ requests, and requirements for your product. It will help you to prioritize and order the ideas and plan iterations easily.
The Backlog board is visually represented with a Backlog Priority Chart. With this chart, you may optimize product priorities by defining important and less important tasks. Be sure, Hygger will also provide you with other useful and interesting options.
It seems that this is all you need if you decide to become a professional product manager. How do you become a product manager? What are your personal secrets? Go forward to your goal and share your impressions!