Dependencies Management
Types and categories of project dependencies in Agile
Browse topics
Everything and everyone is dependent on something or someone. Your summer trip depends on weather and cheap airplane tickets; your colleagues and you are dependent on salary; your working online program highly depends on specific plugins, and so on. Nothing and no one works completely independently.
If we apply this thought to Agile project management, we will see that it a project also has dependencies.

Project managers in any organization think about project dependencies as about the bane. In order to succeed, project managers must counter dependencies in a proper way dealing with different tasks, issues, events, activities, exceptions, uncertainty, and constraints.
So, what is the role of dependencies in modern project management? What are the types and categories of dependencies? How do you show dependencies in a project plan? Which of them is the most common?
In this post, we share the answers and cover other essential facets of the dependency management topic.
What Is a Dependency?
What does dependency mean? This is quite a logical question if you face this topic for the first time.
In general words, dependency is the state of existence of a thing or an item when its stability depends on another thing or item (or any other resource). You may come across a slightly different definition of dependencies, but the essence will remain the same.
What Are Dependencies in Project Management?
In the world of project management, the definition of dependency looks somehow different. A dependency in project management is a logical relationship between two tasks or activities when the completion/initiation of one task is reliant on the completion/ initiation of the other. The main idea is that one activity depends on the other.
Related terms
The following terms are typically associated with project dependency management:
- A constraint is a restriction that determines the boundaries when the task has to be completed. It can be driven by a shortage of time, a lack of money or other resources, or even a lack of expertise. There are 3 constraints in classic project management: cost, time, and scope.
- A Lead is the duration of time that defines when the next activity can be accelerated with respect to the previous activity.
- A Lag defines the duration of time by which the next activity has to be delayed with respect to the previous task. This is actually not desirable in project management.
- A critical path is the longest unbroken chain of sequential activities or dependent tasks. Altering the duration of completion of the items in any way significantly impacts the deadline of the project. That leads to possible violations.

What Is the Role of Task Dependencies in Project Management?
When you plan your projects, software dependency management is what you really need. Luckily, modern software solutions allow simplifying and automating a lot of things. Even project managers without experience may use Gantt charts and online Gantt tools to visualize dependencies. When PMs know every dependency in their project they are able to easily allocate the right resources to the right tasks at the appropriate time. Additionally, these charts help to plan and meet deadlines.
What Is the Importance of Dependency Management?
Why dependency management is critical? It is simple: if you do not care enough about dependency management, your project can go sideways fast. For example, what if your task can’t start as planned because the one it was dependent on wasn’t finished in time?
5 Reasons to Encourage Project Dependency Management
You may logically ask, “Why should I use dependency management in project management software?
Nowadays, dependency management is critical for controlling and managing the interrelated tasks or processes that have to be completed to deliver the clients’ requirements.
Dependency management functionality in your PM software will assist you to:
- prioritize tasks, activities, resources, and processes so that the projects get completed in the shortest period with maximum efficiency;
- get the shortest path followed in the project for its completion;
- manage the natural demand for resources;
- deliver quality products to customers;
- maintain efficiency in the project.
What Are the Types of Project Dependencies?
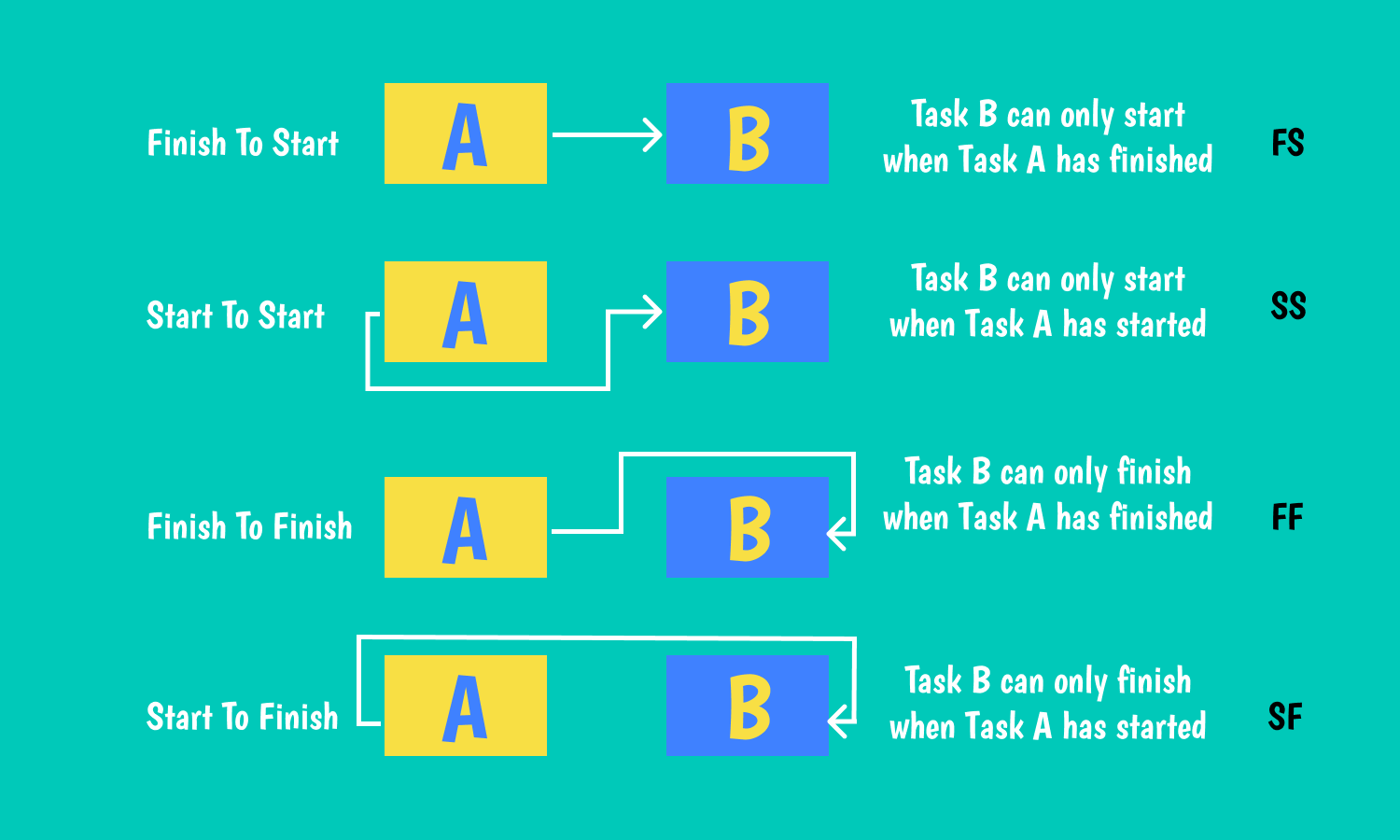
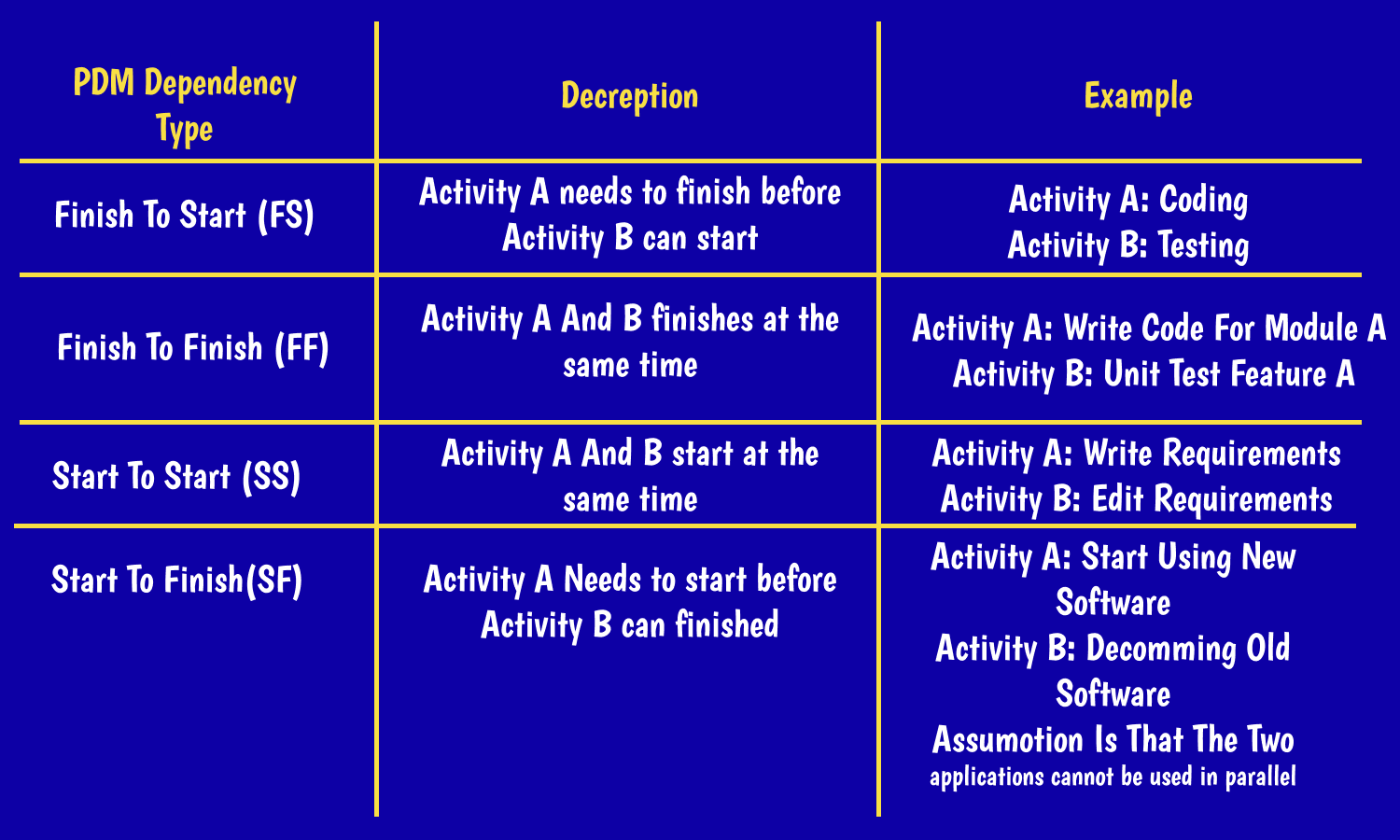
Classical project management defines four types of dependencies that reflect relationships between tasks:
- Finish-to-start dependency means that you have to complete the 1st task before the 2nd task can start.
- Finish-to-finish means dependencies when the 2nd activity can not be completed until the 1st one has been done.
- Start-to-start dependency means that you can not commence the following task until the 1st one has started.
- Start-to-finish is when the 1st task has to start before the 2nd activity can be completed.
What Are the Categories of Project Dependencies?
You can categorize software dependencies in a number of ways based on the initiation and completion of tasks, the relationship of tasks to the project, and other conditions.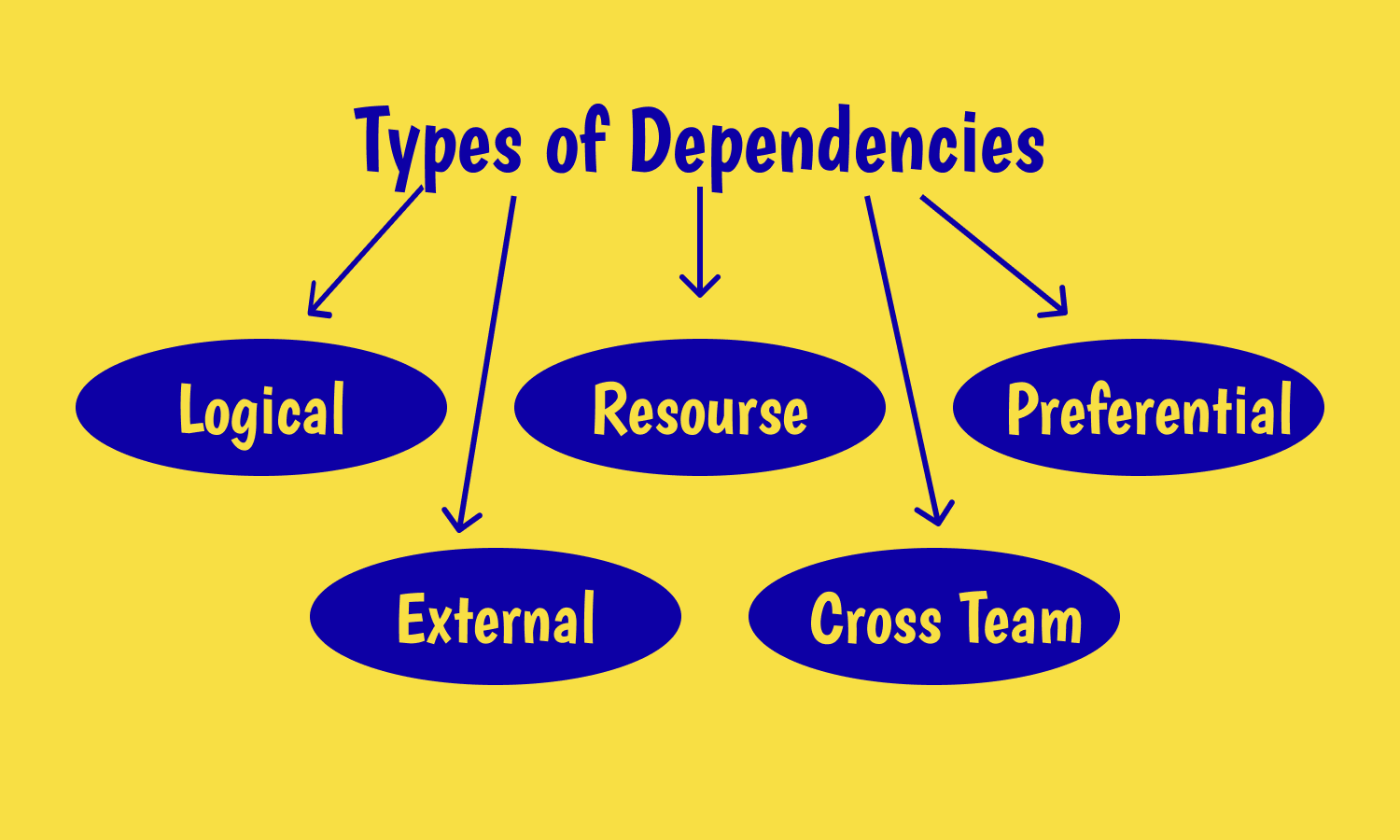
Project dependencies categories are logical, preference, and resource-based:
1. Logical dependencies represent fundamental requirements.
2. Preference dependencies are based on the preferred path although they have several schedule options.
3. Resource-based dependencies allow you to complete them more quickly if additional resources are available.
4. External dependencies remind us that there are things bound to be out of our control no matter how much we plan. This is about activities that are dependent on outside factors and project managers can’t do anything to influence their progress.
5. Cross-team dependencies mean that sometimes multiple teams work on a single, complex project and they rely on each other to complete the project on time.
The following types are also often defined:
6. Causal dependencies can be found in the natural flow of tasks within your project. Each task is dependent on the completion of the previous one. So, avoiding one step in the process will lead to a failed project.
7. Outside/inside dependencies mean that certain tasks may have a combination of both internal and external dependencies.
The Grid System of the Outside/Inside Dependencies
Dependencies of tasks can be internal to a project and external to the company (or vice versa). Here’re some common combinations of dependencies:
- Company in/project in – are applied to sequential tasks that you have to tackle according to a pre-defined logic.
- Company in/project out – can be applied to activities that are taken care of by other departments.
- Company out/project in – when activities are delegated to 3rd-party suppliers. The outcome has a direct relation to the project, however, the vendors are not employed by the organization.
- Company out/project out – there is a factor outside the company and the project but it can negatively impact deliverables.

Reason for Dependency
| Reason for Dependency | Consideration | Example |
| Requirement dependencies – exist due to the requirements of the project being built. | Agile teams should strive to identify these dependencies during the planning process, in order to plan accordingly. | A new road bridge must meet all building regulations and codes. |
| Expertise or SME (subject matter expert) dependencies exist as the work requires specific expertise of a subject matter expert and cannot be performed without the input of someone with this expertise. | When there is someone with this expertise in the team, the dependency is internal and easier to manage. When it is external and required often, the team should consider adding someone with this expertise. | Because a bridge is built on a steep slope, engineers must be sure that it will withstand all weather conditions. |
| Business process dependencies mean that one step must be performed before another to fulfill business requirements. | They need to be considered in pre-planning to ensure that operational processes are not overlooked. | Before the beginning of the bridge construction, a loan must be procured to pay for building the bridge. |
| Technical dependencies exist due to technical limitations or constraints. | Can not be uncovered until work has started. All work involving technical requirements should also be included in the pre-planning process. | Because the bridge is built on a slope, it must utilize different drainage systems and architectural reinforcements. |
What Are the Benefits of Dependency Management in Project Management Software?
It seems that it is impossible to try eliminating dependencies completely. Some of them are even necessary for effective collaboration, risk management, and technical reasons.
Agile teams always strive to reach more agility and their goal shouldn’t be to eliminate dependencies entirely but to improve flow, and increase their ability to predict how project dependencies examples will impact their ability to deliver work.
Visualizing connections between related work helps Agile teams unlock greater levels of agility, by:
- Improving workflows.
- Reducing context switching at every level.
- Optimizing work sequencing to prevent roadblocks and reduce process waste.
- Assisting teams in setting more realistic expectations with stakeholders.
- Improving cycle and lead times.
- Practicing more effective prioritization within and across teams.
- Reducing process variabilities.
The more the Agile team cares about dependencies management, the more skilled it becomes.
How to Tackle Dependencies Effectively?
If you have a powerful project management tool, its functionality will probably include task dependencies and related views.
- Discuss possible project dependencies and associated constraints. If you face many dependencies and constraints, you will be able to go ahead and identify the critical path (to be focused on the tasks that can impact the bottom line).
- Engage with stakeholders. Make sure they understand the most important dependencies and constraints. If the critical path components are included in the project charter, then the stakeholders automatically know about them.
- Arrange brainstorming to discuss the risks associated with these dependencies and constraints. Consider multiple perspectives. After feeling that you have covered foreseeable disruptive circumstances, move ahead and find solutions to manage the impact of disturbances on the dependencies and constraints.
Tips on How to Identify Project Dependencies and Constraints
Using the following 5-step approach for identifying project dependencies and constraints, you will get closer to the entire success of your project.
1. Creating a log of project dependencies
Start with a brainstorming session and document all the dependencies that have an impact on your project. Use an available template or create your own one to set up a dependency log. Outline who is exactly responsible for managing the dependency and all the other important information including whether it is an internal or external dependency.
2. Creating a log of project constraints
Arrange the same brainstorming and document all the constraints that have an impact on your project. You may apply the same doc as you used to record the dependencies.
3. Adding the major dependencies/constraints in a project initiation doc
Add the major dependencies and constraints to your PID (project initiation document) to have all essential information about the project in one place. If your log contains many entries, consider which ones have the highest priorities and only include them. Your goal is to be sure that all stakeholders have a full understanding of the project environment, and dependencies and constraints are two key elements of that.
4. Creating a risk log
Define the dependencies that may seem like project risks. Outside-the-project dependencies are typical contenders for being moved to the risk log. Some constraints (for example, limited access to people for user testing) also look like risks, so make sure they are recorded as well.
5. Choosing the way of how to track dependencies and constraints
You should have a clear way to assess the dependencies and constraints on a regular basis so that you can manage their impact on the effective delivery of your project. In case you have external project dependencies, agree with the project manager on how to let each other know when things change.
Top Tools for Managing Project Management Dependencies
- Gantt charts are used for the dependencies planning and execution with the schedule.
- PERT charts are applied for prioritizing the tasks and breaking down the work into smaller tasks. They require using a circle or rectangles for the help of nodes or milestones in the project.
- Kanban boards with handy cards are utilized to streamline the process and avoid wastage in projects.
- CPM (Critical Path Method) is used to identify the shortest path to complete the project considering the duration of tasks and their dependencies.
- Logic network shows the sequence of the activities to be planned and executed over time.
Final Thoughts
Project management dependencies are not a bane. Using an appropriate dependency management tool, every team or large enterprise in any sphere can efficiently manage and control dependencies within a project.
Professional PM software will improve work processes by helping you eliminate bottlenecks, dependencies, and constraints while improving the overall workflow and cycle time.
How do you deal with project dependencies in your projects? Do you document dependencies separately? Please share your thoughts with us.