Agile Product Management
All you should know about product management in the Agile environment: defining product roles, vision and strategy, best practices, components, and essential benefits. All in one place.
Browse topics
Striving to find the best product management definition, you will have some challenges as it is defined very differently in every single company.
However, many organizations all over the world have worked to generate a unique product management definition that can be applied to all spheres and company types. Especially companies that preach the principles of Agile.

Product management is the intersection between business, technologies, and user experience. It also involves more functions with the aim to create value for customers and the business.
So, what does product management mean? What are the phases of the product life cycle? Read on to learn more about what product management exactly is, how product managers work, and what is needed to build products people will love.
Read on below
Product Management Articles
Product Strategy
Reliable ways and tips to set your strategic vision for the product offering.
Read this Article
Product Planning
How does the planning process affect how you drive your product development?
Read this Article
Product Roadmap
A visual source of truth that outlines the vision, direction, and progress of your product over time.
Read this Article
Product Manager
An ultimate guide to the core aspects of the product manager job.
Read this Article
Product Requirements Documents
A quick guide to writing a product requirements document.
Read this Article
Product Features Prioritization
How you can use product features and prioritization techniques to develop and launch truly efficient products.
Read this Article
Net Promoter Score
Measuring customer experience and predicting business growth with the help of NPS - Net Promoter Score
Read this Article
Product Analytics
What product teams need to know about product analytics
Read this Article
Idea Management
What is idea management and how to make the process of ideation more effective?
Read this Article
Remote Product Manager
Why product management can be even more effective when done remotely.
Read this Article
Lean Project Management
Why apply Lean in project management?
Read this Article
[Continued]
What Is Product Management?
What is the product management process? Product management is the process aimed to bring a new product to market or develop an existing one. It begins with an initial idea about a product that clients will interact with and ends with the delivery and the product evaluation.
Product management is a combination of business, development, marketing, and sales efforts; and this combo can significantly benefit companies.
Effective product management contains creating and documenting a product strategy. It is settled down somewhere in the very center of an organization and aimed to balance the need to deliver value and profit to the company with the clients’ requirements and technical possibilities.
As many products – so many challenges related to them that require a unique approach to product management.
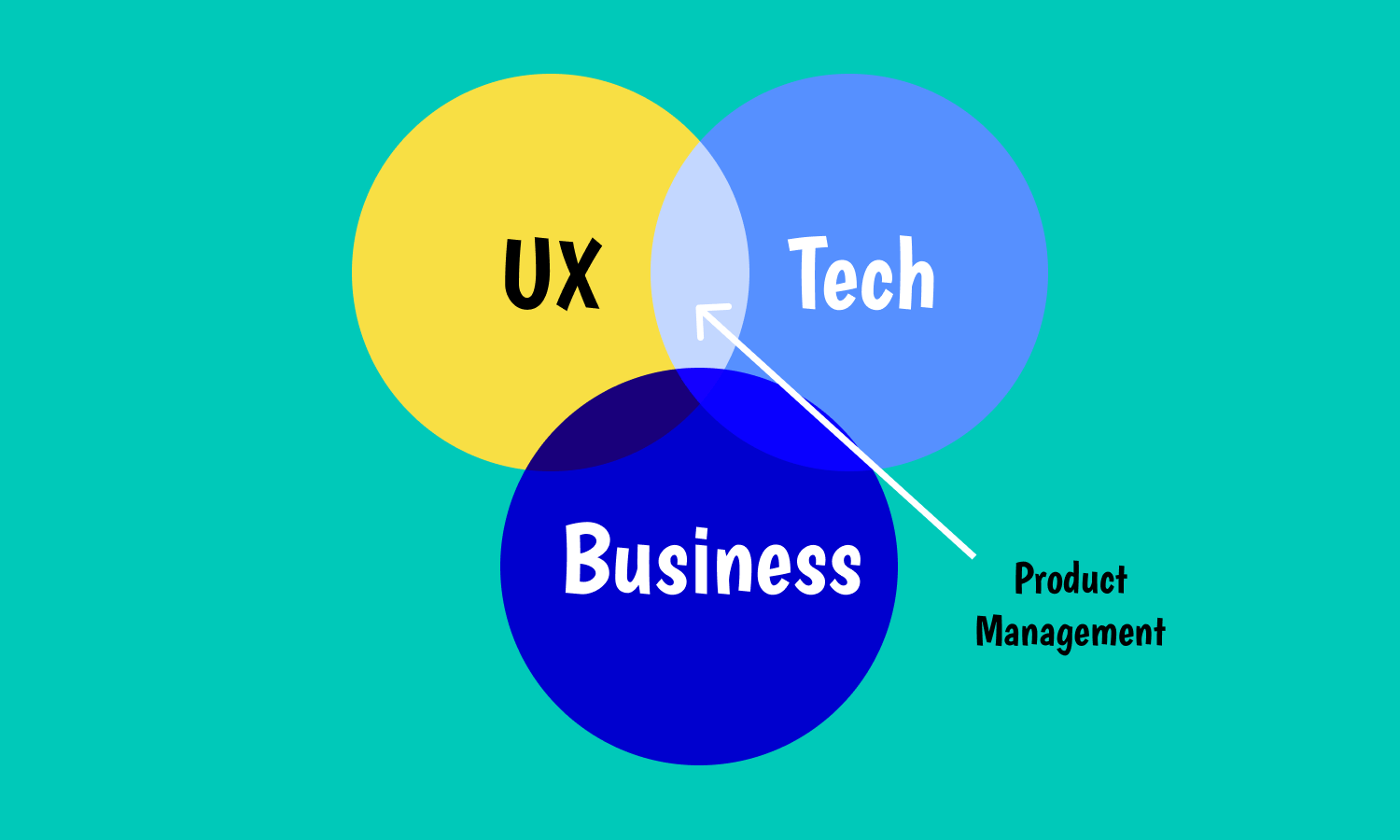
PM can be considered as the intersection of business, technology, and UX:
- Business. It means that product management helps teams to reach their business goals and objectives by minimizing the communication gap between development, design, business, and clients.
- Technology means that PM happens in the engineering department on daily basis. So it is critical to understand computer science.
- User experience. It means that the PM is focused on the UX, and represents the customer inside the organization.
What Is Agile Product Management?
In Agile, the process of product management requires guiding a product through multiple iterations.
Agile software development provides a more flexible approach to product management. The scope of an Agile project is fluid, while resources stay the same, so the Agile team spends less time defining the product, and it is more open to changes.
Agile product management guides developers through cycles while maintaining the vision of the product and integrating customer insight. Product managers in the Agile environment are more integrated into technology teams than business teams.
Product Management Origins
The roots of product management go deep into a brand management concept. In 1931, Neil McElroy, an advertising manager, initiated the idea of a job with specific responsibilities to manage the product’s brand and be accountable for its success.
This concept today largely determines the modern approach to product management. Over the next half-century, a lot of companies all over the world introduced this brand management approach.
In the 1980s, many principles of such a consumer product management approach were adopted by the software market in line with its growth. By the way, later McElroy became the president at P&G as well as at Harvard University.
Over time, product management and its organizational benefits became more and more coveted. Many brand managers went on to become entrepreneurs and product leaders.
In the 1990s, the gap between brand management and engineering widened. In 2001, the famous Agile Manifesto was delivered, which broke down department silos and outdated processes, so a unified product management role got a separate room.
What Are Product Management Goals?
The product management discipline pursues 3 fundamental goals:
- To get higher profitability, build once and sell many times. This will provide economies of scale.
- To deliver efficient products that customers will buy, always be an expert on the market and the product.
- To have a balanced view across all the different aspects of the product, lead the business.
What Are Product Roles?
Different businesses have different approaches to product management. It depends on the organization’s size, the industry, whether you work with physical products or software, and whether you sell to consumers or businesses. The varieties of product management don’t end there.
PM may involve lots of job titles that are focused on various activities related to the product.
The most common PM jobs are:
- Product manager
- Product owner
- Marketing product manager
If these roles overlap and are implemented differently from one company to another, this may confuse a lot.
Internal and External Responsibilities of Product Managers
The responsibilities of product managers include internal and external responsibilities.
- Internal PM involves customer research, competitive intelligence, and considering industry trends.
- External management is about marketing responsibilities, branding, customer communication, PR, events, advertising, as well as product launches.
What Is Not Product Management?
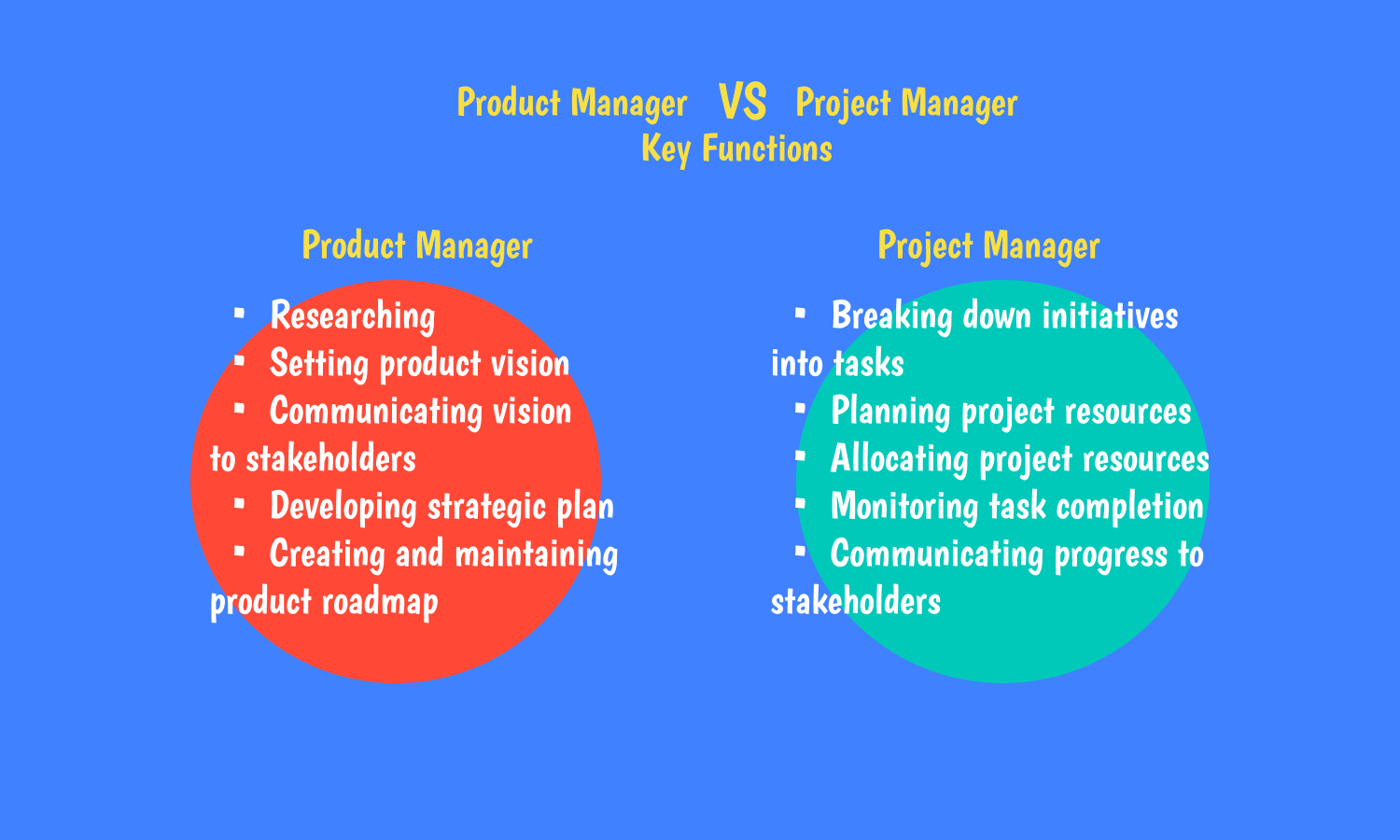
There is a common misconception about product managers who own the routine and everyday details of a product’s development. This is actually about the role of a project manager.
Product management relates to a strategic function, and product managers are responsible for communicating product plans and goals for the rest of the company. Their constant headache is to ensure that everyone in a team is working toward a shared organizational goal. And they should not be responsible for any detail of the development process.
Modern businesses assign tactical elements such as managing workloads and project management scheduling. They understand that the distinct division will leave the product manager free to focus on the higher-level strategy.
Why Is Product Management Important?
Effective product management will definitely help you in case you care about:
- Building high-quality products. There are always many more ideas for products than available funds for them. The goal of a product management team is to prioritize the ideas for potential products to let them focus on the most profitable ones. Product managers track all solutions to define their effectiveness. They also evolve or cancel the ineffective products to enable the team to focus on high-value products.
- Providing the right product features at the right time. When you have several delivery teams that are working in parallel, they will experience functional dependencies between the products being worked on. You should consider these dependencies when prioritizing to make the proper functionality be available when it is needed.
- Ensuring that people use the product. Marketing issues are also an essential part of product management. When individuals do not know about available functionality, they are unlikely to buy or use it.
Product Management Life Cycle
What are the 6 stages of the product life cycle? The product management process contains the following stages:
- Vision development
- Market and customer research
- Developing a strategy
- Product development
- Marketing and sales
- Tracking metrics
All phases may contain inbound and outbound activities, and the role of a product manager is to supervise the fulfillment of all activities, but not necessarily perform them.
1. Vision development
One of the most important parts of product management is product vision. With its help, you can define the final product and understand the direction towards achieving it. This is the initial point where the strategy starts and the team discusses a new product.
It’s better to formulate the product vision during a brainstorming session, setting the goals for the product and defining specifications.
2. Market and customer research
This phase can occur simultaneously with the first or precede it. Market and customer research is a process of collecting and analyzing required information about the market and potential customers. During this stage, you have to compare similar products that already exist, study rivals, and identify your target audience.
When you know your client, you’ll be able to build a successful product. That’s why product managers in cooperation with product marketing managers conduct different research to have a deep understanding of potential product users.
This research may include the following perspectives:
- Studying customer behavior, understanding your clients in terms of their motivations and overall psychology.
- Identifying customers’ needs in order to deliver the product that will be in demand.
- Creating user personas, describing fictional characters that represent the user types that can have interest in the future product.
With the help of market and customer research, organizations can understand what clients want and develop a strategy for creating an efficient product.
3. Developing a strategy
After defining a vision, having enough knowledge about the market, and customers, you need to formulate a specific product strategy.
A product strategy describes a way to achieve defined goals and set key milestones. It must include a clear and reliable plan for the team that works on a product. Your strategy for a product will define the core features, users, and KPIs that the product must meet.
One of the best ways to visualize a product strategy is to use a handy roadmap that will allow a team to control the work at all stages. The roadmap will provide a framework for the team with friendly timelines and specific actions, illustrating the vision, goals, and the current state of product development.
One more significant responsibility of the product manager during the strategy development stage is a thorough prioritization. All the objectives aims, and activities on a roadmap must be ranged from the most to the least important.
When the strategy is developed, the PM should communicate it to the team and all stakeholders.
4. Product development
This stage is devoted to teamwork on the product itself. Product development includes testing (internal and external) and the application of feedback.
It all starts with defining technical specifications and making the first prototypes. The UX team often assists. For product managers, it must be crucial to identify what the users want in order to communicate this info to the project manager and the development team.
Another important responsibility of the product manager is defining the MVP (minimum viable product) and making sure it serves its purpose.
The PM can use A/B testing for evaluation. It helps to choose the product features that are more useful to the customers (or provide higher customer engagement).
5. Marketing and sales
It is time now to enter the market. This phase is devoted to marketing and launch plans. Sales teams should be trained to start distribution.
There are three essential aspects of an effective product launch:
- Boosting customer awareness with different marketing campaigns and promo activities.
- Choosing a proper pricing strategy (based on competition and the product’s value).
- Defining the appropriate release timing considering customer readiness.
A successful product marketing strategy contains many pre-launch activities that are focused on creating a buzz effect around the product. This will involve various media channels, high-quality content, SEO, pre-launch giveaways, etc.
6. Tracking metrics
The only thing the product manager needs now is to monitor its progression and analyze data to evaluate the success of a product.
There are key metrics that can be organized into the following groups:
- Financial metrics
- Metrics that demonstrate user engagement
- Metrics that reflect user interest
- Metrics for measuring the product’s popularity
- User satisfaction metrics
It is not enough to just select the metrics and collect the required information. You have to care about further analysis and valuable insights. They will show the top management how well the product performs and if any changes are necessary.
The Evolution of Product Management Tools
For many years, product managers over the globe used a combination of spreadsheets, text docs, and simple presentations to communicate their product strategy and roadmap. These instruments are available and usually included in professional suits of applications of many organizations.
However, over time, it became clear there was a need for special tools and solutions.
Luckily, modern SaaS solutions and cloud-based apps make it possible to generate strategy, define features, manage releases, and capture customer feedback in a single place.

What Are the Elements of Effective Product Management?
As in many other disciplines, product managers find their professional way by following the paths of those who practiced before them. And as usual, experienced PMs have plenty of lessons to offer the newcomers.
Effective product management requires special skills that can lead you to success. Here they are.
Communication
Communication skills top the list of successful PM characteristics as so many job aspects rely on prowess in this area. Additionally, product managers should be great listeners to solicit and gather feedback. They should be able to exhibit significant customer empathy.
Working with stakeholders is another critical point that is not less important than communication with engineers, architects, and quality assurance teams. In order to build a fabulous user experience, product managers must also collaborate with UX designers. So, the key to delivering exceptional products is nurturing a true partnership with all the parts.
Tech background
How technical must product managers be? Of course, they must have some level of technical understanding and special skills. PMs must provide meaningful dialogue with engineering. They should be knowledgeable enough to use their product and relate to the clients it’s intended to serve.
In companies where there is an actual need for PMs with in-depth tech skills and knowledge, they can always hire a technical product manager to fill that role.
Business orientation
Product managers are integral to making sure that a product is strategically and financially successful. This begins with defining goals and the vision of the product. One of their duties is translating those ideas into the tactics required to make them a reality.
It is also important for them to care about finding product-market fit and assessing requests from customers. Product managers must also be good at metrics, applying data-driven decision-making to move the product forward.
What Are the Ways to Optimize Product Management Operations?
As we know, time is a precious commodity. Therefore, product managers must always be efficient and organized to conduct the necessary meetings and dialogs. To get through decision-making promptly, they must find an appropriate way to get to an agreement quickly.
By the way, product managers often borrow some useful skills from their project management counterparts, and this practice is quite good. They must be always aware of how to carve out time for critical tasks and create an environment where they can concentrate.
What Is the Disciplined Agile PM Mindset?
According to the principles of the Agile Manifesto, we can define several Agile philosophies that are critical to success in product management. Here are some commandments of these philosophies:
- Be customer-driven. The needs and desires of customers should drive your PM decisions.
- Understand the full value stream. Addressing the full value stream that your product is part of from the very start to end from the client’s point of view is really important.
- Use an experimental approach. Often, it is useful to go beyond asking people for their needs if you want to recognize what to offer your clients.
- Practice incremental releases. When you release smaller increments more often, you have a chance to reduce the feedback cycle with your clients.
- Embrace changes. Competitors enter the market constantly, customer desires change rapidly, and new technologies are introduced often. Professional PMs should be able to accept it.
- Plan strategically. You should always plan your products strategically in the long term and implement them tactically in the short term.
Wrapping up
There are countless products released each year, and unfortunately, a large percentage of them fail. The causes are different but a truly significant one is that too many products are not thoroughly prepared for market conditions.
Neglecting even a small aspect of product development may lead to financial losses. Proper product management is what will help you to evade such consequences and increase the chances of the product succeeding in the market.
