Agile Project Management
How to implement Agile project management considering Agile principles, practices, and roles.
Browse topics
Agile methodology greatly increases a project’s prospects for success. It is geared toward continuous improvement, and more and more businesses realize that Agile adoption will continue to increase across different industries around the world.
We tried to cover the most basic and important parts of Agile project management.
If you are planning to transit your team to Agile, this method's principles, processes, tools, roles, and artifacts will help you change your mindset and begin performing collaboratively to be more flexible and adapt to changes as they come.
Agile is not for everyone. However, teams that implement it correctly experience outstanding benefits, including streamlined work processes and rapid innovations.
Read on below
Project Management Articles
Kanplan
How to plan Kanban with Kanplan
Read this Article
Project Plan
What are the rules of creating a powerful project plan?
Read this Article
Agile Program Management
What is the role of program management in the Agile environment?
Read this Article
Project Dependencies
Everything you need to know about managing dependencies in Agile projects
Read this Article
Agile Workflow
The rules of creating a healthy workflow for Agile projects
Read this Article
Agile Stories, Epics, Initiatives, And Themes
Comparing user stories, epics, initiatives, and themes in Agile projects
Read this Article
Agile Epics
An ultimate guide about Agile epics: everything you need to know
Read this Article
User Stories
How do user stories help to make better products?
Read this Article
Story Points Estimation
The principles of using story points estimation in Agile projects
Read this Article
Agile Metrics
How to apply the best Agile metrics to measure your project efficiency?
Read this Article
Gantt Charts
Using handy Gantt charts to improve managing Agile projects
Read this Article
Project Portfolio Management
Everything you should know about project portfolio management in one place.
Read this Article
[Continued]
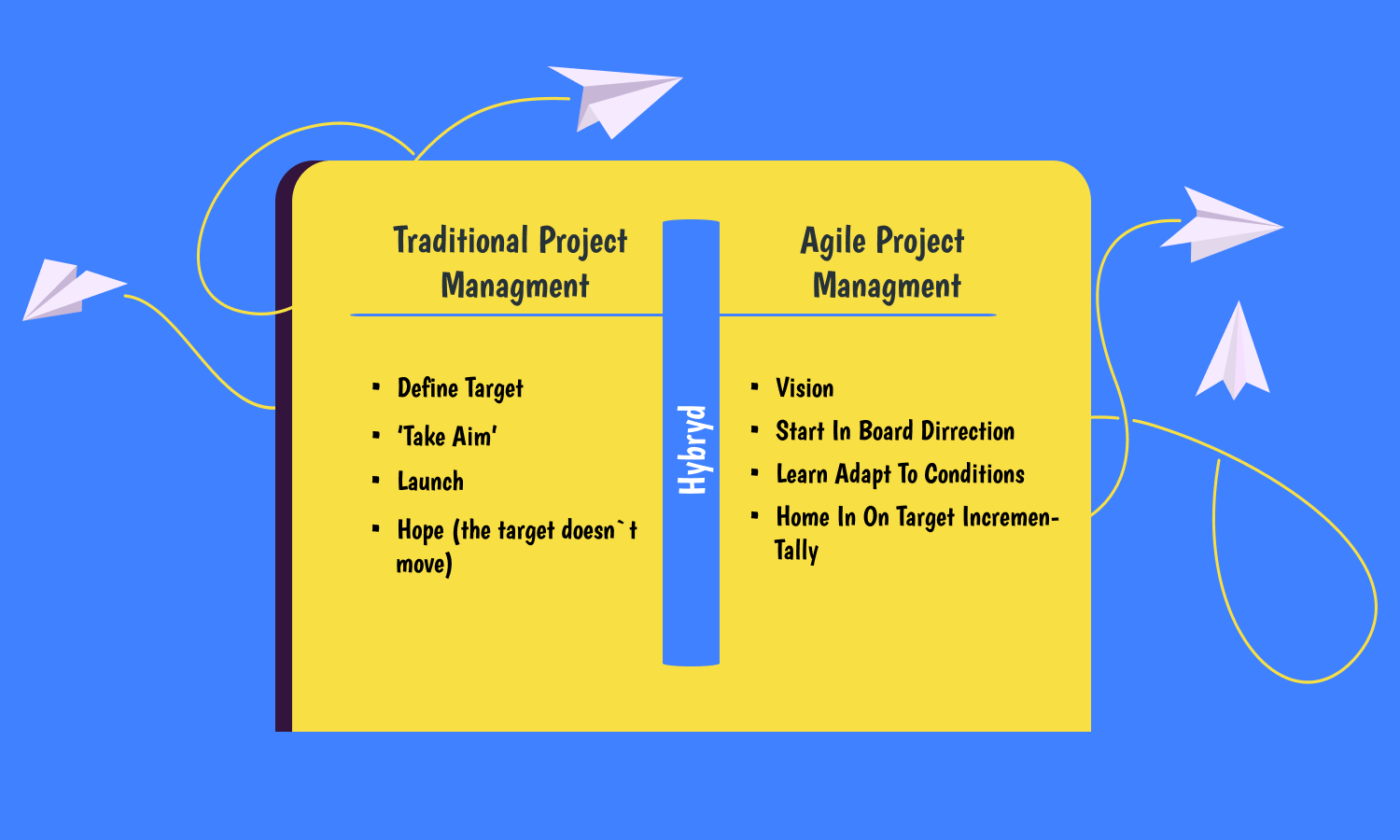
What Is Agile Project Management?
Agile project management (APM) is a popular iterative approach to delivering a project during its life cycle.
Agile life cycles contain several iterations or incremental steps towards the project completion. This iterative concept is frequently applied in software development projects to promote velocity and adaptability. That’s all because the benefit of iteration allows adjusting as you go along rather than following a linear path.
The iterative approach of Agile project management methodology is aimed to release benefits throughout the process rather than only at the end. In fact, Agile projects should demonstrate core values and behaviors of flexibility, trust, empowerment, and collaboration.
Key Historical Facts About the Agile Project Management
The XXI century has demonstrated a fast rise in the use of the Agile management methodology, especially for software development projects and various IT initiatives.
However, the roots of the continuous development concept date back to the mid-20th century. These roots took different forms, championed by many leaders over the years.
We can recollect the RIPP (Rapid Iterative Production Prototyping) approach developed by James Martin. The approach served as the premise for the book Rapid Application Development written in 1991 and the approach of the same name — RAD.
Scrum is the separate Agile PM framework that has evolved in more recent years. The method features a Product Owner who collaborates with a development team to create a product backlog with a prioritized list of features, required to deliver a software system.
Top List of the Popular Agile Methodologies
The most frequently used and popular Agile methods are Scrum, Kanban, and Lean. Other methodologies include:
- Scrum
- Kanban
- Lean
- XP (Extreme Programming)
- Crystal
- DSDM (Dynamic System Development Model)
- FDD (Feature Driven Development)
- ASD (Adaptive Software Development)
- AUP (Agile Unified Process)
- Crystal Clear methods
- Disciplined Agile delivery
- Scrumban
- RAD (Rapid Application Development)
Who Are the Users of APM?
As we know, Agile was initially created for software development. However, the approach was quickly adopted by more than just the IT sector. Healthcare, education, construction, as well as marketing agencies and the automotive industry representatives, are also looking at the Agile method and its frameworks to deliver innovative products in uncertain environments. Many companies can get benefits from Agile project management, as it is easy simple to set up and use.
In software development, the end product may be hard to define. Due to its flexibility, Agile PM allows for that ambiguity.
What Are the Agile Team Roles?
Some of Agile methodologies require specific team roles to adhere to the framework, such as:
- A Scrum Master (SM) acts as a team’s advocate. He/she ensures that every sprint stays on track and helps to remove/resolve any issues or challenges that may come up. They are the team’s advocates.
- A Product Owner (PO) defines the goals of a sprint, manages and prioritizes the team backlog. PO is the voice of the customer or internal stakeholder.
- Team Members (usually of three to seven people) are the ones who execute the work in every sprint. They can be composed of different specialties or people with the same job roles.
- Stakeholders should be up-to-date on the product and sprint goals. They should also have a chance to review and approve work during a sprint and provide feedback. Stakeholders are an informational role only.
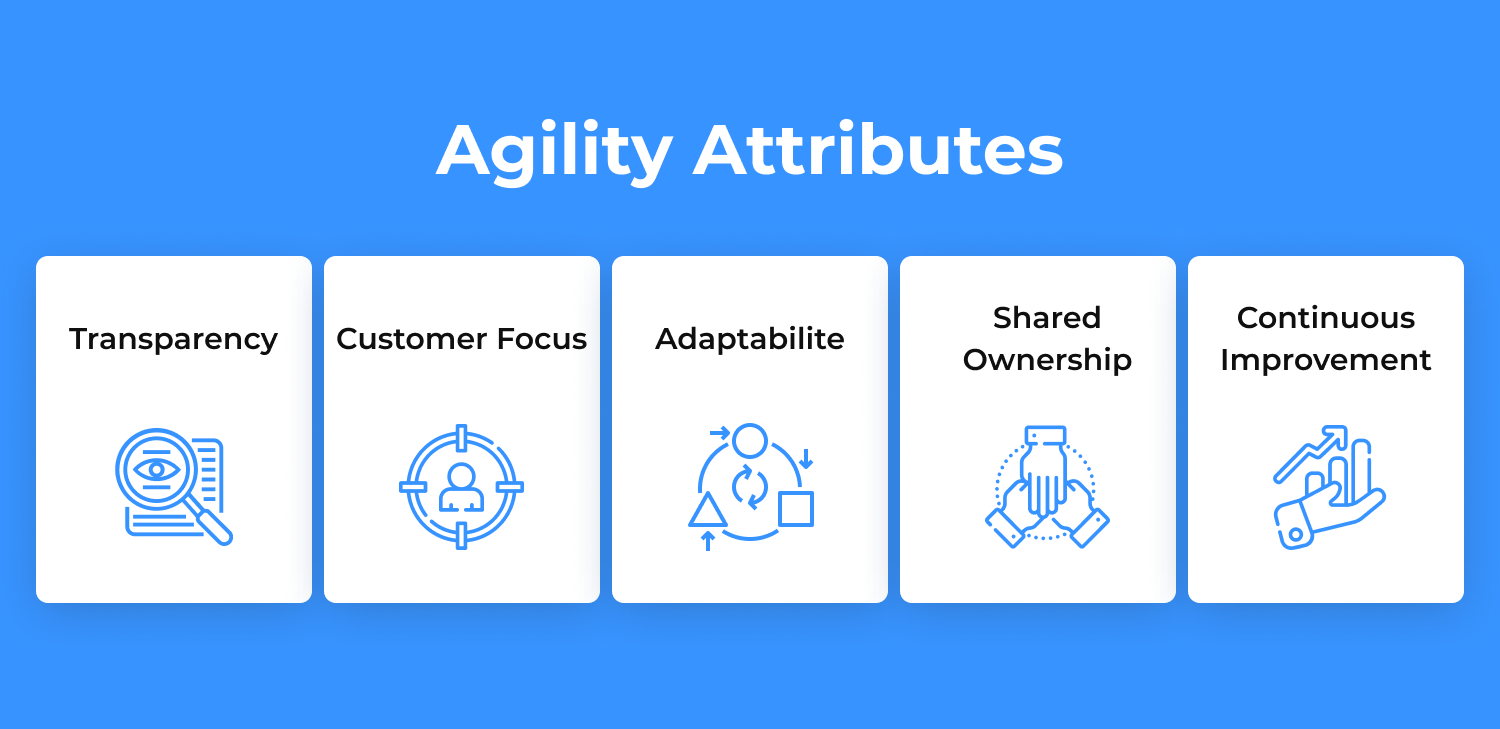
Five Attributes of Agility
The term “agility” is at the core of the Agile project management concept. This word means mobility and nimbleness that signifies the ability to move something forward in a quick way allowing to change the direction.
Agility in project management has five essential attributes that form the building blocks of the Agile process:
- Transparency
- Focus on customers
- Adaptability
- Effective Leadership
- Continuous Improvement
Let’s take a closer look at each one of them below:
1. Transparency
A shared understanding of the process among all concerned parties is crucial in Agile project management. It requires increased transparency in the way teams communicate and perform work.
Team members should be able to openly share their work progress by integrating information radiators such as handy Kanban boards. With their help, everybody can understand what their colleagues are doing, how they are doing it, and how to do it better.
Additionally, people involved in Agile practices should freely share their ideas without feeling concerned that this might compromise their status in the project. Therefore, the Agile approach aims to create an environment in which team members collectively work toward the solution.
2. Focus on customers
You can produce the best solution in the world but if your customers do not see how it will help them to solve a particular problem, they will not want to use it. That’s why a heavy focus on ensuring customer requirements is very important in the Agile approach to project management. You should provide your clients with not just what they asked for but what they really need.
There are frequent feedback loops in the Agile project delivery lifecycle. They are like checkpoints where clients can see how “what they wanted” actually looks like. This leads to the exploration of possible innovative solutions and new knowledge.
3. Adaptability
Instead of producing one big batch of work, the Agile methodology is focused on an iterative approach where teams break down their projects and deliver small chunks of them. It allows them to keep flexibility for the remaining work.
It is critical to ensure that what is being worked on is synchronized with the end-user. It will allow you to capture any changing customer requirements early in the process, avoid delays, and adapt to the new situation.
The adaptation phase includes short project reviews with the customers who give their respective feedback. The main idea here is to adapt your future actions based on that feedback and apply small modifications to what has been delivered instead of doing extensive rework.
4. Effective leadership
Another essential Agile PM attribute is the instilment of a sense of ownership within teams. It contributes to leadership that is more effective.
Agile projects provide team members with a large fragment of the decision-making process. It is worth actively including them in the planning processes and letting them decide how to execute their tasks best.
Agile encourages team members to collaborate and solve problems based on their understanding instead of waiting for the Agile project manager to say what has to be done. This motivates and empowers individuals to be more effective in their work. They contribute in the best possible way toward successfully completing the project.
5. Continuous improvement
Agile project management creates an environment for continuous improvement and this is also rather important. Agile teams have an opportunity to be regularly engaged in frequent learning cycles alongside project development. It guarantees that process improvements will occur while the Agile project is still in motion. It will lead to the successful delivery of the final solution to the end customers.
Additionally, as the work is broken down into small deliverables, these chunks are handed over to clients for their feedback, which also contributes to the continuous refinement of a product.
What Are the Agile PM Phases?
The Agile project delivery process can be summarized in five typical phases:
- Envision is about creating a high-level product vision for clients and defining who will be involved in the project.
- Speculate is an extension of the first phase. Team members collect the initial broad requirements for a product and develop an iteration plan based on the vision.
- Explore contains the work on the project deliverables with a focus on flow. This is about getting feedback from the customer as fast as possible.
- Adapt means reviewing delivered results and adapting them to current conditions.
- Close is the conclusion of the project and the key findings.
Estimation, reporting, and planning
In order to plan future work or sprints, you’ll need a way to see your team’s progress. Agile project estimating is what helps Kanban and Scrum teams in understanding their capacity. Reports demonstrate the team’s progress over time and backlog grooming (refinement) helps project managers to keep the list of work current and ready to tackle.
- Agile estimating is a crucial aspect of both Scrum and Kanban project management. Scrum-focused teams use project estimating to identify how much work can be done in a particular sprint. Kanban teams set WIP limits for each state based on their previous experiences and team size.
- Agile reports (for example, Burndown charts) show how many story points are completed during the sprint. Many software solutions offer out-of-the-box reports with real-time, actionable insights into how your teams are performing.
- Backlog grooming helps teams to reach their long-term goals by adding and removing items based on the team’s long-term capacity and changing business objectives. Using a modern project management software system, you’ll be able to groom huge backlogs with multi-select ranking and order user stories and bugs by dragging and dropping issues.
What Are the Key Components of Agile Project Management?
User stories
A user story is a definition of a work request that includes enough info for teams to make a reasonable estimate of the effort required to accomplish the request. Stories are written from the user’s perspective and are focused on outlining what the customer client wants.
Sprints
A sprint is a short iteration, usually between 1-3 weeks, when Agile teams work on projects’ tasks. The main idea is to continuously repeat these sprints until the product is feature-ready. At the end of the sprint, you review the product readiness and make adjustments.
Stand-Up
A Daily Stand-up is a meeting that usually lasts 10-15 minutes. This event is a great way to ensure everyone in the Agile team is on track and informed. The ceremony is known as a Stand-Up because the attendees are required to stay standing, helping to keep the event short and to the point.
Agile board
Agile boards (physical or digital) help the team track the progress of the project. One of the great examples is a Kanban board or a separate function within modern project management software.
Product backlog
Project requests become stories in the backlog. During the planning meeting, the team estimates story points to each task. The stories in the backlog are moved into the sprint to be completed during the iteration. Managing a backlog is a significant mission in Agile project management.
Essential principles of an Agile way of working
Agile concentrates on empowered people and their interactions. The method also focuses on constant value delivery. Agile project management is about delivering maximum value against business priorities in the budget and time frames allowed. Here’s a list of the key Agile project management principles:
- The Agile project is broken down into smaller pieces. They should be prioritized in terms of importance.
- The Agile project intends collaboration, especially with customers.
- The Agile project is adjusted at regular intervals. This lets customers always be satisfied with the outcomes.
- The integration of planning and execution is what is included in the Agile methods. It allows companies to create a working mindset that helps teams to respond to changing requirements efficiently.
What Are the Most Important Agile Project Management Events?
- Brainstorming – an effective way to solve current tasks, based on stimulating creative activities. During the session, a team generates as many ideas as possible and determine the best solution based on them.
- Project Planning – the Agile ceremony that includes creating a product vision statement and a product roadmap.
- Release Planning represents planning the future product features. During the meeting, Agile team members identify a product launch date.
- Sprint Planning is a meeting at the very beginning of each sprint. The goal of the ceremony is to identify a sprint goal. Team members also discuss the requirements that support this goal.
- Daily Stand Up is a short event aimed to synchronize actions and discuss statuses on short-term tasks.
- Sprint Review is arranged at the end of each sprint and introduced by the Product Owner. During the meeting, developers demonstrate the product functionality completed to stakeholders. The PO collects feedback.
- The Retrospective is one more meeting at the end of each sprint. Agile teams discuss what went well and what they could change. This is the time for making a plan for implementing changes in the next sprint.
The list of Agile Project Management Advantages
What are the benefits of Agile PM?
- Increased flexibility and adaptability
- Focus on customer needs
- Optimized development processes
- More rapid solutions’ deployment
- Faster turnaround times
- Faster detection of various defects
- Reduced waste due to the minimization of resources
- More focused efforts that lead to increased success
- Increased frequency of feedback
- Optimal project control
What Is the Process of Transitioning to Agile Project Management?
Once you trust Agile project management, you’ll want to start by educating your team on how they will transition into their new roles, when they will have daily meetings, and how they will transition their current work into the Agile environment.
After establishing all transition steps, you’ll logically want to track people’s progress and success. Monitoring a new Agile team’s progress will be beneficial to giving it confidence in the changes.
Use special Agile metrics to justify the benefits of transitioning a team to Agile when in higher-level meetings.
Are There Any Organizational Hurdles to Adopting Agile?
Yes, there are some common hurdles, that companies looking to adopt Agile for project management may encounter:
- Unclear understanding of the impact on the business goals. Remember that strategic alignment is still critical.
- A company’s structure that does not support Agile. Your project team may be ready for Agile development, but the rest of the organization may not be on board.
- Rushed testing cycles. Sprints can create a risk of rushed testing cycles. Defects can go undetected or are detected too late.
- Limited Agile skills. It is often difficult to find top Agile talents. Limited Agile talent means limited benefits for the organization wanting to execute projects using this approach.
What Is the Future of Agile Project Management?
Today Agile offers numerous benefits to various businesses as competition is continually increasing and time to market is shrinking.
More and more organizations make the shift to digital workplaces, which are highly dependent on flexibility, speed, and advanced productivity. Consequently, the Agile approach will become increasingly useful. Its application in multiple industries indicates that Agile adoption rates will continue to increase across different spheres around the globe.
Conclusion
We tried to cover the most basic and important parts of Agile project management.
If you are planning to transit your team to Agile, this method’s principles, processes, tools, roles, and artifacts will help you change your mindset and begin performing collaboratively to be more flexible and adapt to changes as they come.
Agile is not for everyone. However, teams that implement it correctly experience outstanding benefits, including streamlined work processes and rapid innovations.