Kanban Cards
Get started using powerful Kanban cards more competently
Browse topics
If you are starting to read this post, then you probably already know something about Agile software development and a famous Japanese word — Kanban. The Kanban methodology is not going to lose its popularity, and this post will dwell on a small but very important part of the system — Kanban cards.
What Is a Kanban card?
A Kanban card visually represents how a work item moves through different completion stages on a physical or online Kanban board. This key element of the Kanban system reflects work that has been requested or that is already in progress.
What Should Be on a Kanban Card?
Each Kanban card contains valuable data about the task it represents. It includes the task status, summary of the assignment, deadline, responsible person, and so on.
The card helps teams to visualize work, regulate work in progress with WIP limits, and maximize the flow.
To quickly understand the idea of the Kanban card system, imagine a software development team that use a whiteboard and sticky notes to represent their work items.
Like every dev team, they have different features and bugs. They move the sticky notes through defined columns (for example, To Do, Prioritized, Development, Testing, Blocked and Done).
It demonstrates that any Kanban card template is aimed to visualize assignments’ progress from the moment they are requested to the moment they can be considered as done.
During the development process, Kanban cards perform in the following way:
- inform about every tasks’ step,
- reduce the number of additional meetings,
- improve the transparency of work processes,
- help to avoid context switching as the number of cards that are in progress should be limited.

Kanban Cards Quick History
Any concept has its own history, the Kanban card is no exception. In Japanese, Kanban means “visual signal” or “signal board”. Kanban cards were invented in the 1940s. Their creator, Taiichi Ohno was an industrial engineer at Toyota company. He was looking for ways to improve Toyota’s manufacturing process and the result of his creation was a Kanban system with convenient cards.
One day Taiichi Ohno discovered an interesting thing during shopping in a supermarket. The supermarket managers re-stocked shelves instead of keeping inventory fully stocked at all times. It was obvious that one of the shelves was nearly empty, so the store replenished that shelf with enough merchandise.
Ohno noticed that this kind of just-in-time (JIT) delivery would revolutionize the manufacturing supply chain. He decided to visualize various manufacturing processes on the factory floor. A Kanban card was a great solution right for this aim. Visualizing the card that included full info about the required quantity, part specifications, and delivery time, suppliers could clearly fill the order and send the restocked bin with its Kanban card back to the factory floor.
Toyota used this secret for a long time and only in the 1990s, people took notice and the company began sharing the Kanban card system concept details.
What Is a Kanban Inventory System?
The Kanban inventory system uses handy cards of different colors to distinguish different items and to stock and promote the placing of new orders as particular items decrease in number. This system allows teams to boost production efficiency and is often associated with Lean manufacturing.
Lean manufacturing preaches the continuous flow of products. Superfluous amounts of inventory in the Lean environment lengthen the cycle time for any part of the production flow. The increased cycle time for any part is a waste in Lean. When a company stocks a high level of inventory, there is a chance to keep defective materials for a longer period before its discovery.
What Are Two Types of Kanban Cards?
There are two types of Kanban cards: physical and online. When it comes to modern Agile software development, digital Kanban boards examples and Kanban cards examples surely look more efficient and beneficial.
Physical Kanban cards limit you in the way how many details and info you can write on each card. It is harder to analyze work item metrics there.
For this reason, using smart project management software to create online Kanban boards is highly recommended.
What Is Kanban with Example?
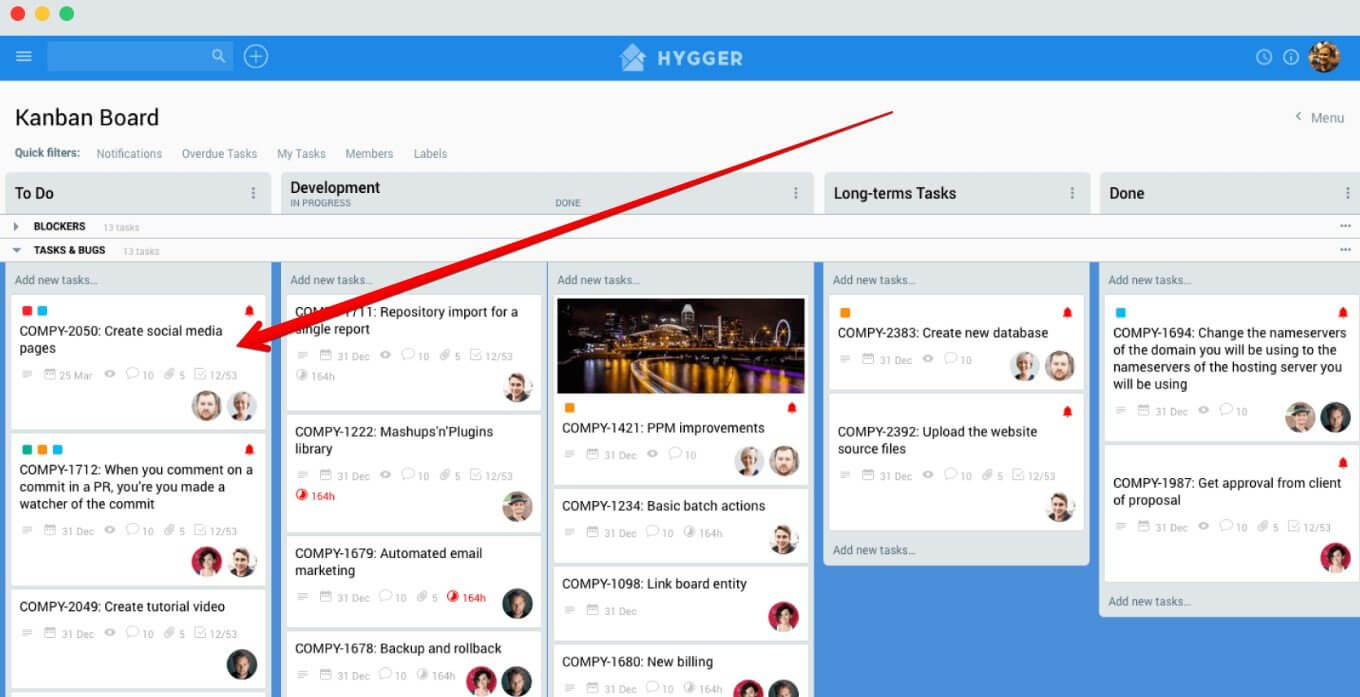
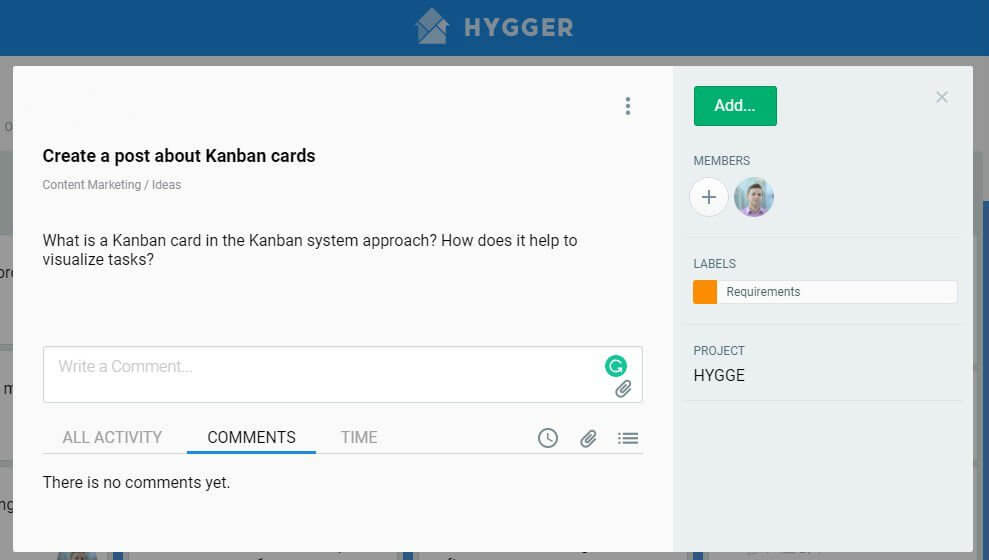
Kanban theory is quite simple and straightforward. However, it is always easier to understand any concept by visualizing it with a good example. Here is what a typical online Kanban board template with cards from Hygger.io looks like.
How Does an Online Kanban Card Look Like?
The typical elements of Kanban cards examples are:
- A title (or a unique item number)
- Item description
- A rough estimate of the work size
- The number of items to be moved
- Location information
- Lead time
- A responsible person
- The due date
- A class of service
- Priority, etc.
What Are the Key Purposes of Kanban Cards?
Kanban cards assist team members to communicate and share information visually, encouraging effective teamwork. They allow to:
- View important tasks details at a glance. It’s about statuses and due dates, task’s owner, and other relevant info.
- Run deliverables efficiently. With the help of Kanban card templates, teams can establish clear and consistent expectations for each functional area.
- Improve productivity and efficiency. Using Kanban boards with cards you can track lead time, the time it takes for a work item to go from start to finish. Kanban cards also help you to identify bottlenecks in workflow and streamline their process.
How Does a Kanban System Work?
What key rules and steps should we consider while working with online Kanban boards and cards? To start working with a Kanban card, you first need to create a board. It does not matter whether it is digital or physical.
Using a powerful project management tool such as Hygger.io, you are able to choose a Kanban board template and customize it to suit your specific project.
This tool looks great for project management in many industries: construction, IT, marketing, finance, education, and many more. Define the number of columns you need and name them.
The typical Kanban board example will have three columns:
- To-do
- In progress
- Done
Then you have to create a Kanban card for every task of your work. It is possible to create a Kanban card template for recurring work items and similar tasks.
After filling the Kanban card template with the required information, you need to make sure everyone in your team knows how to move the cards through the columns. Everyone is responsible for moving their tasks through the columns, identifying bottlenecks, and making suggestions for improvement.
What Are the Core Benefits of Kanban Cards?
1. Detecting inefficiencies
Kanban cards easily define when there’s a problem with one of the steps in a work process. The team will quickly get a queue if it consistently has twice as many cards in the Testing column as in Design and Development. The possible solution is to hire more testers.
2. Facilitating JIT (just-in-time delivery)
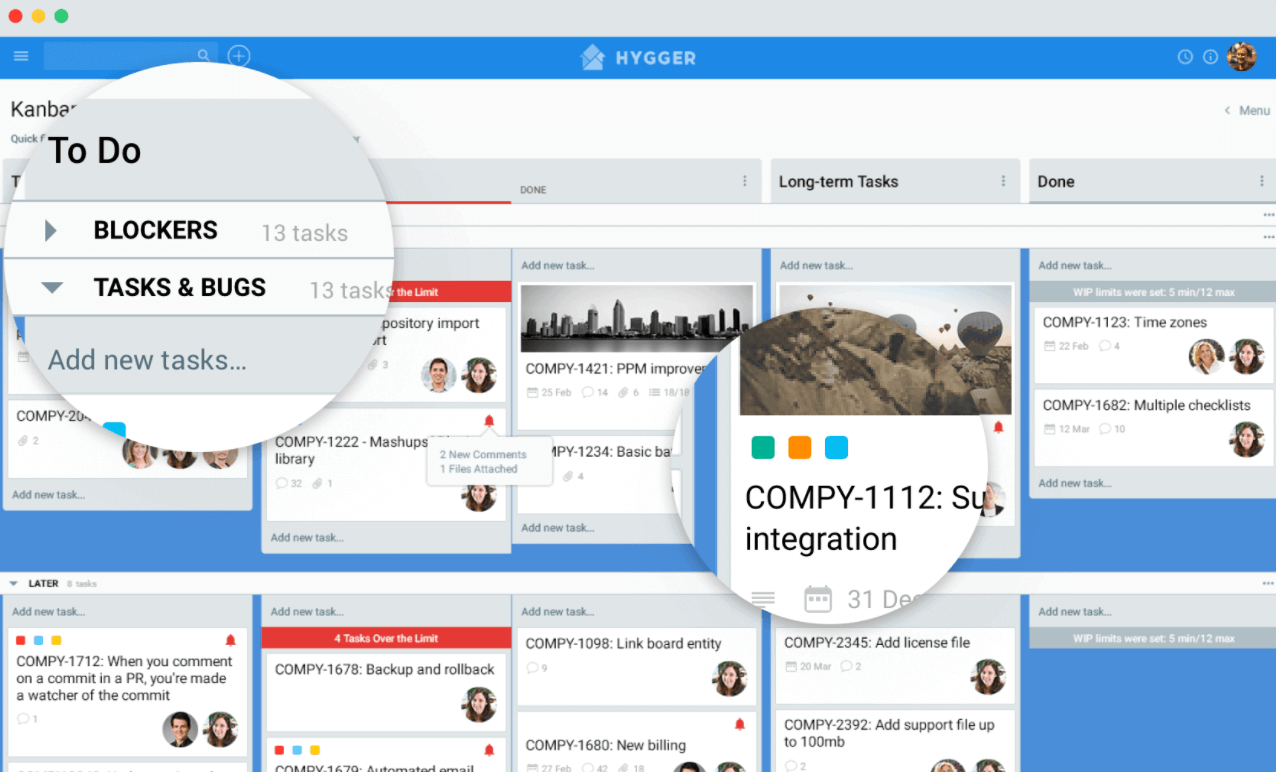
The JIT concept is useful in various industries other than manufacturing, including software development. A great solution that helps teams to avoid stagnant projects is a work-in-progress (WIP) limit option. It’s important to limit the number of cards at any stage of a workflow at one time. When a Kanban column is maxed out, team members work to move those projects to completion before they can take on new work.
3. Encouraging collaboration
Kanban boards and cards are sharable. As cards advance from column to column, they pass from team to team or from a particular employee to another one. Although everybody is responsible for a different part of the process, they all are looking at the same thing and can collaborate.
What Are the Risks Related to Kanban Cards?
- You should treat a Kanban card like a controlled item because a lost card can cause a shortage.
- Kanban cards require a stable environment.
- Outdated Kanban card examples lead to stock-outs, so try to always keep them updated.
- If extra items are hidden, it means that Kanban cards are not showing the correct quantity.
- All types of Kanban cards manage inventory but do not reduce it.
Final words
All Kanban cards examples are aimed to simplify the life of software development teams as they make problems highly apparent. If you are not using Kanban cards yet, test them first to define all the nuances of their use. No matter what industry you represent, the Kanban system with convenient cards will help you organize your work items and get your job done efficiently.
If you want to dig deeper into the Kanban world details and its artifacts, study our Agile 101 page.