What is the Project Life Cycle: Defining Key Project Management Phases

Project managers know that there may be dozens of tasks that need to be completed at just the right time and the right sequence. They will confirm that it’s rather easier to handle the details of a project and take steps in the right order if this project is broken into phases.
What is the Project Life Cycle in Project Management?
The project lifecycle is a set of phases that a project undergoes from initiation to closing. This also includes different activities necessary to fulfill all the project’s objectives.
What are the phases of project management?
Project phases help to plan and control projects. Every phase in the project life cycle has similar tasks and leads to a major deliverable.
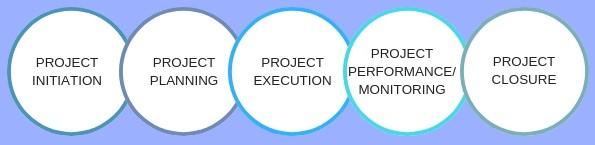
There are 5 main phases that can help to give your efforts structure and simplify them. They correspond to the project management process groups in the PMBOK.
Project management phase 1. Initiation
The very first phase of any project lifecycle is Initiation when the value of the project and feasibility are measured.
During this phase, project managers should perform the following:
- define a scope of work.
- define the resources needed to complete tasks
- determine the timing to complete the tasks
- define the project cost.
- create an action plan
- define the project’s progress reporting requirements against budget, time, and project scope.
- create a communication plan
- identify project risks
- plan how to coordinate with stakeholders and so on.
Typically, the following evaluation tools to decide whether to pursue a project are used by PMs:
- A Business Case Document that justifies the need for the project. It includes an estimate of potential financial benefits.
- Feasibility Study – the evaluation of the project’s goals, timeline, and costs. They determine if the project should be executed. The Study balances the projects’ requirements with available resources to see if pursuing the project makes sense.
Project management phase 2. Planning
When the project receives the green light, it needs a solid plan. This phase of the project life cycle includes a project management plan that is developed comprehensively of individual plans for – project scope, cost, duration, communication, risk, and resources.
Project Planning also consists of several important activities such as making WBS, scheduling, milestones, creating GANTT charts, estimating and reserving resources, planning dates and modes of communication with stakeholders, and so on.
A well-prepared project plan gives the team direction for producing quality outputs, handling risks, and communicating benefits to stakeholders and managing suppliers.
What are the steps for the planning phase?
- Writing a project plan. At this stage, you should define the project timeline considering all the phases of the project, all tasks, and possible constraints. Developing a scheduling management plan is also should be considered here.
- Building workflow diagrams. Here you visualize all processes to make sure your colleagues clearly understand their roles in the project.
- Budget estimation. It is about creating a financial plan where you should determine how much to spend on the project to get the maximum ROI.
- Gathering resources required. Make sure everyone in your team has the necessary tools (hardware and software solutions).
- Anticipating risks and potential roadblocks, and project constraints. Try to outline the issues that may cause your project to stall.
- Running a kickoff meeting. Outline the project and attract all the participants so they can quickly get to work.

Project management phase 3. Execution
This phase of the project life cycle is most commonly associated with the project management concept.
It is when a project deliverable is developed and completed, adhering to a mapped-out plan. Building deliverables should satisfy the customer. Team leaders make this happen by allocating resources and keeping team members focused on their tasks.
This phase relies heavily on the planning phase. Team efforts during the execution phase are derived from the project plan.
Execution is a critical phase as it demonstrates to you whether your project will be a success or failure.
Project management phase 4. Monitoring and Control Phase
Sometimes monitoring and control can be combined with the Execution phase as they often occur at the same time. This stage of the project lifecycle mostly deals with measuring the project performance and progression according to the project plan.
Teams must constantly monitor their own progress to calculate key performance indicators, avoid scope creep, and track variations from allotted time and costs.
This helps to keep the project moving ahead smoothly and prevent project failure.
Project management phase 5. Project Closure
This phase of the project management lifecycle is the logical final when the project is formally closed. Here you face many important tasks such as delivering the product, relieving resources, reward the team members, formal termination of contractors, etc.
When teams deliver the finished project to the customer, complete it to stakeholders, and release resources to other projects, they close the project.
Project Closure is a vital step in the project lifecycle that allows teams to evaluate and document the project and move on to the next one. They keep on mind previous project mistakes and successes to build stronger processes in the future.
Takeaways
Project management is based on the idea that projects go through a number of phases characterized by a distinct set of activities that take the project from conception to conclusion.
Someone may define only 3 phases. However, the number of phases of the project management life cycle is determined by the project team and its certain type.
Have you something to add to this PM’s phases description? Feel free to comment.