How to Explain What is Agile Project Management in a Simple Way
Usually, the phrase “Agile project management” can be heard in office rooms of developers and a product manager’s space. Of course, other team members, clients and partners are aware of what the this includes. However, Agile project management concept hasn’t spread very far beyond the scope of IT industry and not everyone can give an explanation of the term.
In this article, we offer a brief overview of Agile project management for those who need to quickly, briefly and clearly understand what this means.
Perhaps one day you’ll need to explain Agile project management bases to a child, an old lady or a foreigner. Actually, these categories of people, as a rule, require a simple and concise explanation, without unnecessary complex terms and abstract phrases. So let’s press the buttons “Brevity” and “Clarity” and begin to delve.
What is Agile project management?
Long-long time ago…. Ok, not so long. It was 1970 when Agile was first discussed and William Royce published his work on the development of large software systems.
Agile is one of the popular project management methodologies that includes short development cycles. These cycles called “Sprints” and they are focused on continuous improvement in a product or service development.
In 2001, 17 software developers returned to the global discussion and published the Agile Manifesto with 12 principles to guide a people-centric approach to software development.
12 principles of Agile and the famous Manifesto
12 key Agile principles that were discussed by those experts in 2001 are shown here:
Popular Agile Methodologies
Agile is a big family that consists of different methods:
- Kanban
- Scrum
- Lean
- Extreme Programming (XP)
- Crystal
- Dynamic System Development Model (DSDM)
- Scrumban
- Rapid Application Development (RAD)
- Adaptive software development (ASD)
- Agile Unified Process (AUP), and some others.
You can explore the main differences and explanations in our article or, for example, learn how to do Kanban or how to drive Scrum projects with Hygger.io.
The advantages of Agile
In the project management world, Agile is popular among project managers, sponsors, team leaders and customers, as it seems beneficial. The main advantages are:
- Optimized development processes
- Flexibility and adaptability to changes
- The rapid solutions’ deployment
- Optimal project control
- Minimization of resources and reduced waste
- The ability to detect defects faster
- Increased focus on customer needs and specific issues
- Increased team collaboration frequency
- Feedback
What are the roles in Agile project management?
Any successful Agile project planning requires a brilliant team. There are 5 strategic roles in Agile teams:
- Product owner is a person responsible for connecting customers, stakeholders, and the development team. He/she is a product expert and knows everything about customer’s needs and priorities. Product owners work closely with dev guys and seem like customer representatives.
- Scrum master is a person who supports the development team and keeps the Agile process consistent. This role is considered a project facilitator. Scrum masters should have the organizational influence to be effective in a company.
- Dev team that includes people who create a product programmers, designers, testers, tech writers, data engineers, and other people responsible for product development.
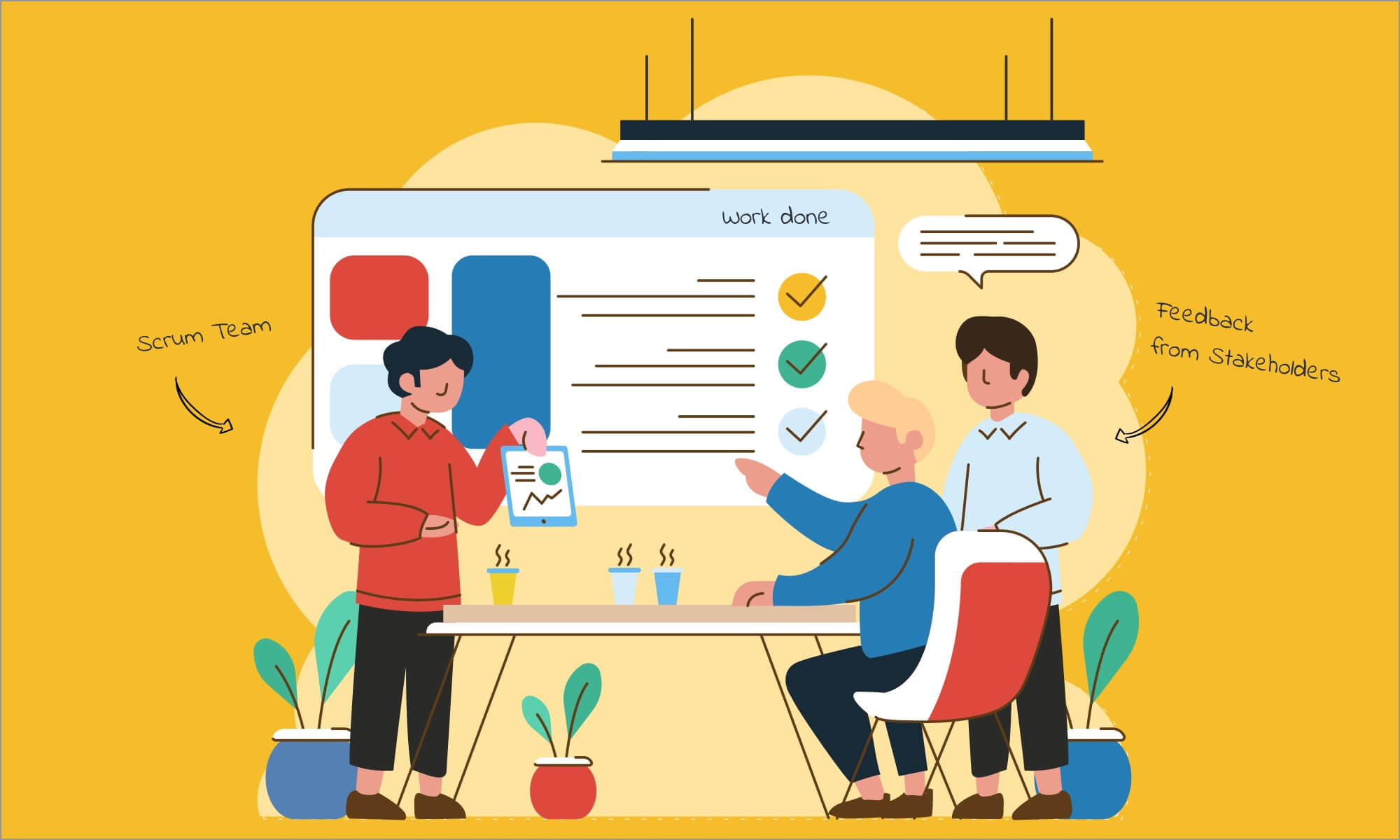
- Stakeholders – people interested in the project. They are not responsible for the product but provide input. Stakeholders can include people from different departments or companies that provide regular feedback and support to the product owner the developers.
- Agile mentor. This experienced expert can share useful insights with the team. In Agile, mentors are not responsible for executing product development.
Agile PM events
Agile projects involve different stages of its life cycle:
- Brainstorming. This is an effective way to solve current tasks, based on stimulating the creative activity of team members. During the brainstorming session, you may generate as many ideas as possible and determine the best solution based on them. The majority of participants in Agile brainstorm are developers.
- Project planning. The process includes creating a product vision statement and a Product Roadmap.
- Release planning. It’s about the planning the future product features. During this planning team members identify a product launch date.
- Sprint planning. Sprint – a short cycle of development that usually lasts 1-2 weeks. It also can be called as Iteration. Sprint planning is one more kind of meeting at the very beginning of each Sprint. The goal of the planning is to identify a Sprint goal. Team members also discuss the requirements that support this goal.
- Daily Scrum or Stand up is a short meeting with the aim to synchronize actions and discuss statuses on short-term tasks. The Stand Up has time constraints assigned by product managers or project managers (most often, 10-15 minutes).
- Sprint review. This meeting is arranged at the end of each Sprint and it introduced by the Product Owner. Developers demonstrate the product functionality completed during the Sprint to Stakeholders. The Product Owner collects feedback.
- Sprint retrospective is one more meeting at the end of each Sprint. Scrum team discusses what went well and what they could change. This is the time for making a plan for implementing changes in the next Sprint.
The artifacts of Agile project management
All project’s stages should be measurable. Usually, Agile teams use the following artifacts to track progress:
- Product vision statement is a quick summary with the aim to communicate how your product supports the company’s or organization’s strategies.
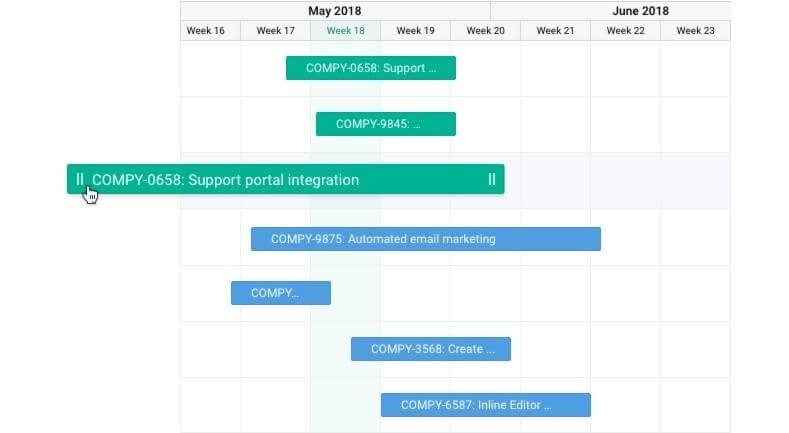
- Product Roadmap – the high-level view of the requirements needed to achieve the product vision. This project tool allows a product manager and team members to determine timeframes to developing and release those requirements. The Product Roadmap is a first cut and high-level view of the Product Backlog.
In Hygger you can share your Roadmap and lay out the high-level perspective of what will happen over time, by specifying major releases, projects, and initiatives.
- Product backlog – a storage for your ideas, customers’ requests and requirements for your product. It helps to prioritize and order the ideas and plan iterations easily.
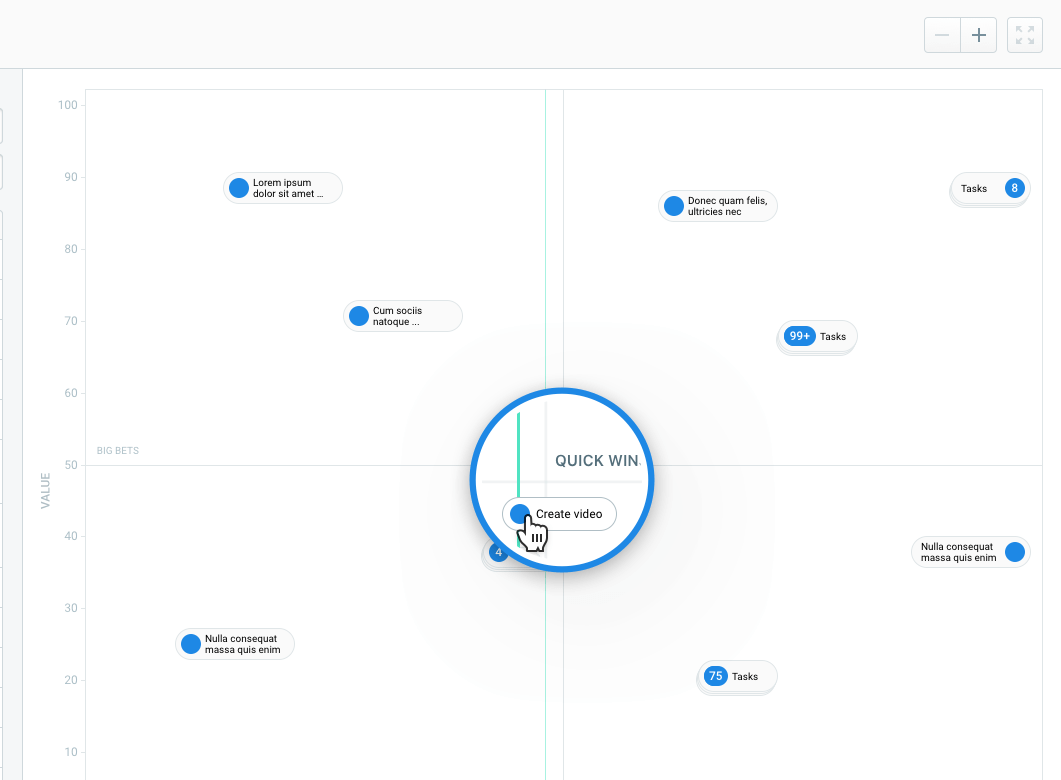
Hygger assists to set up Value and Efforts parameter for each idea. Comparing Value & Effort combination of each task will help you prioritize the tasks better and choose the most important tasks for development.
A great visual representation of a Backlog board is a Backlog Priority Chart. This tool will help you to optimize product priorities by defining important and less important tasks. In Hygger you may find 4 segments on the chart: Time Sinks (tasks are not worth working on at the moment), Maybes (tasks that do not bring a lot of value but are easy to implement), Big Bets (tasks that can bring a lot of value but are as well hard to implement), Quick Wins (these tasks are valuable and quite easy to implement).
- Release plan – a timetable for the release of working software.
- Sprint backlog that includes the goal, user stories and tasks associated with the current Sprint.
- Increment. This is the working product functionality, demonstrated to Stakeholders at the end of the Sprint.
As we see, Agile offers numerous benefits. Of course, there are some limited drawbacks but it’s a topic for a separate article.
The application of Agile methods in multiple industries indicates that Agile adoption rates will continue to increase across industries around the world. What do you think about it?