How to Make Requirements Management Effective?

A clear expression of requirements is an essential part of final product success. The requirements may be expressed as physical deliverables, business benefits, functional or technical needs. Sometimes a weak Requirements Management process can be a cause of a product failure.
In this article, we try to define how smart Requirements Management can address the causes of project and product delays and failures and contribute to product success.
What are requirements in product management?
In simple words, Requirements Management is the process of capturing, assessing and justifying all wants and needs of stakeholders.
Requirements are all capabilities that your product must meet to satisfy users’ needs and desires and to solve their problems. Users’ needs may come from business or market needs, legal regulations, industry problems, competition, and so on.
Requirements classification
In product management, all requirements can be divided into functional and non-functional requirements.
- Functional (business) requirements are fundamental capabilities of the product that should satisfy specific user needs.
- Non-functional requirements are connected with usability, reliability, performance, and security – the must-have qualities for any product. They also include technical requirements.
The power of Requirements Management
All doubtful requirement issues in the product lifecycle should be addressed very early because even a small design problem based on poor requirements may lead to global design issues.
What are the reasons for project failure?
Different research studies demonstrate the following reasons for project failure: lack of resources, incomplete requirements, unrealistic expectations, no users participating, poor planning, lack of managerial support, changing requirements and so on.
Actually, requirements issues are not the most common reasons for project failure, however, they need to be resolved as early as possible.
In today’s Requirements Management’ reality, project and product managers try to highlight requirements issues as they arise. The truth is – the most of these requirements issues can be found and resolved during the early stages of project development. To be honest, sometimes it’s not easy, as many requirements processes require the clients’ participation.
How does a well-specified requirement look like?
It should be:
- clearly identifiable
- understandable
- relevant to business needs
- consistent (to not contradict any other requirement)
- traceable
- verifiable (can be verified, tested and be appropriate for analysis)
- prioritized (to have clear importance).
4 processes of Requirements Management
Requirements Management includes the following processes:
- Requirements planning
- Requirements development
- Requirements verification
- Requirements change management
Requirements planning consists of development, review, and the requirements plan approval. The plan should be reviewed and approved by all stakeholders including clients, dev team, managers and team leads and, of course, the sponsors.
Requirements development is requirements gathering, their definition, and deep analysis. All requirements can be known or unknown. The goal of the gathering process is to collect as many known requirements as possible. Here you should pay attention that clarifying and prioritizing the information can be very time-consuming.
The definition process includes organizing, documenting and defining all requirements.
Requirements analysis is closely tied to the gathering and definition. The main goal of requirements analysis is to discover unknown ones.
Requirements verification is the stage of ensuring that all stated requirements are being satisfied. The process includes the user acceptance testing and validation and the analysis of how the requirements are being addressed in the development plan.
Requirements change management is about the implementation of a change control system and managing the actual changes. This process is closely connected with the requirements development and the verification process.
What is a Product Requirements Document?
It’s a good way to start working with requirements and ideas by fixing them in a special doc – in Product Requirements Document.
A Product Requirements Document (PRD) is a kind of visual document that contains the basic product functionality under development. The document also helps product managers to define the order and any task conditions for the project.
Product manager’s tasks and concerns can easily turn into a cycle of entangled issues that can lead to terrible consequences. Therefore, it’s better to start with a high-quality PRD document to avoid routine in product management tasks and to deal with confusion.
There is a difference between PRD and Market Requirements Document (MRD). The distinction between two concepts is quite simple: MRD describes the opportunity or market needs, while PRD is connected with a product, which addresses that opportunity, or needs.
Why is a Product Requirements Document important for managers?
It is rather convenient to always have a complete picture of what is happening before your eyes. PRD is an overview of the key important details that needed for the potential project development. The document includes key goals, objectives, principles of implementation, expected results, required time and any additional technical requirements. When product managers elaborate product requirements in this document, they can anticipate and avoid possible issues from arising.
Why does a successful product manager need a product requirements document? The main goal of PRD is to define the product you want to create: from its purposes to the features and functionality.
This document is not the private stuff of the product manager because it should be shared with technical and business teams.
The well-designed PRD provides clear direction toward a product’s purpose while creating a shared understanding among business and technical teams.
PRD advantages and disadvantages
It’s easy to highlight the evident advantages of a high-quality Product Requirements Document. However, there are those who note some drawbacks. Here they are.
PRD pros
- It combines every step in the full picture of the product, with the choice to include or exclude some features and detect any potential problems timely.
- It visualizes time needed for project development processes.
- It assists to understand the budget required for the development processes.
- It evolves a mutual comprehensive understanding between clients and dev team.
PRD cons
- Extra time, spent by a manager to identify and list all the specifications that are required for the project.
- Extra money for developing a detailed document with all specifications.
What does a high-quality PRD template require?
Here’s a list of components that every Product Requirements Document should have. Each section of this template is important in its own way. And when they all form a cohesive whole, the result can transform your product management workflow:
- Objectives
- Key components
- User Flow
- Details on each user flow step
- Analytics
- Future features
How to create a great PRD?
Certainly, every point depends on your product and its complexity but be sure that every step may be adapted.
Objectives
The very first step in the way of creating the document should be associated with your objectives. Here you propose a background information to your readers. It’ll help them understand what the product is.
Think of the following: who is the target audience for your product, what the global problem you try to solve, what are the goals of the product and so on.
You mustn’t have any doubt, just a clear understanding of what is needed, and how your product will address that need.
It’s up to product manager to create a clear and concise value proposition to easily communicate to everyone: team members, executives, customers, sales managers, etc.
Components
On this stage, you need to list the key parts of the product feature. It will give your readers a picture of what will be the rest of PRD focus on.
User flow description
User flow is a stage where you define a consumers’ step-by-step path. This stage should include the details about how users get through each step of the path.
Details
After defining objectives, components and user flow, it’s a high time to determine the specifics of each page. You should outline all elements of the feature you are working on — and all of the different states that may exist.
Analysis
Team collaboration is crucial while writing your PRD. It’s also important to understand what your users are doing to have a chance for improving the features. You should work with different types of questions and hypotheses to analyze your product.
Future features
Defining the future features your team will understand how the product can evolve over time.
As a product manager, you definitely have more product insights than others have. That’s why you should share this knowledge to help the team to get everything faster.
If we say about effective requirements management, we mean that it obligatory involves all 4 processes mentioned above and applying a well-designed PRD.
Nowadays you may find different techniques and smart services that assist managers to work with requirements processes: the tools for organizing and documenting requirements, available templates for defining requirements, tools for reporting, gathering, testing, and requirements verification.
You can distribute some of the processes even in a simple Google Doc or using Excel. The more complicated but rather convenient way is to use a special platform, for example, Confluence.
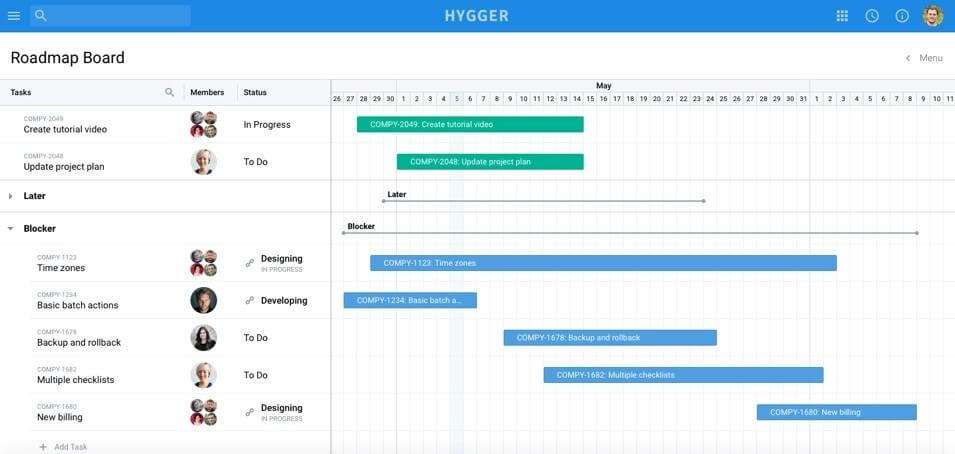
You may also create the PRD and share it with the help of Hygger Product Roadmap. It assists to visualize your ideas and product initiatives and share them with the team within the preparation of product requirements.
A Roadmap will cover all your management needs, lightweight the way to capture product strategy, requirements, and communicate with the team.
It does not matter if this strategic tool is used by an Agile product manager, or if it is a marketing roadmap, its functionality will be sufficient to implement long-term strategies and daily plans.
Conclusion
When requirements are being properly curated and managed there is clear product understanding and consistent communication between the product team, developers and stakeholders. The process of requirements management also involves adjustment to requirements changes throughout the course of the projects.
The more detailed you work on your Product Requirement Document, the better you will describe the product you are building. It will help your team including sales and marketing departments to piece the puzzle together.