What is Critical Path Method For in Project Management?
All project managers have their best practices and management methods, own secrets and tricks. They try to improve their processes for effective results using intuition, skills and experience, powerful tools and famous techniques.
Recently, we’ve described the most popular project management methodologies, and now it’s high time to share the rich details of one of them – the Critical Path Method.
*the article was originally published on DZone
How can a critical path help in project management? Actually, what does it mean? What is the special method about?
Critical path in project management
A critical path in project management is certain tasks that need to be performed in a clear order and for a certain period.
If part of one task can be slowed down or postponed for a term without leaving work on others, then such a task is not critical. While tasks with a critical value cannot be delayed during the implementation of the project and are limited in time.
Critical Path Method (CPM) is an algorithm for planning, managing and analyzing the timing of a project. The step-by-step CPM system helps to identify critical and non-critical tasks from projects’ start to completion and prevents temporary risks.
Critical tasks have a zero run-time reserve. If the duration of these tasks changes, the terms of the entire project will be “shifted”. That is why critical tasks in project management require special control and timely detection of risks.
CPM: What are the roots?
The method was developed by one of the American companies in 1957. Its employees planned to close, repair and restart chemical plants. The tasks in this project were numerous and complex, that’s why they required such a method. After that, Critical Path Method was quickly spread to agricultural and construction projects where people wanted to learn how to avoid routine tasks. Today, this method of identifying critical tasks is widely used in many industries, including software development.
6 Benefits of Critical Path Analysis
Critical path analysis is required in order to predict the timing of project’s completion.
Here are 6 main advantages of CPM:
- The method visualizes projects in a clear graphical form.
- It defines the most important tasks.
- Saves time and helps in the management of deadlines.
- Helps to compare the planned with the real status.
- Identifies all critical activities that need attention.
- Makes dependencies clear and transparent.
What are the limitations of Critical Path Method?
It is believed that the methodology was developed for routine and complex projects with the possibility of a minimum change in the completion time of tasks. CPM loses its usefulness in more chaotic projects.
There are alternatives, for example, PERT-diagrams, which allow changing the duration of each activity.
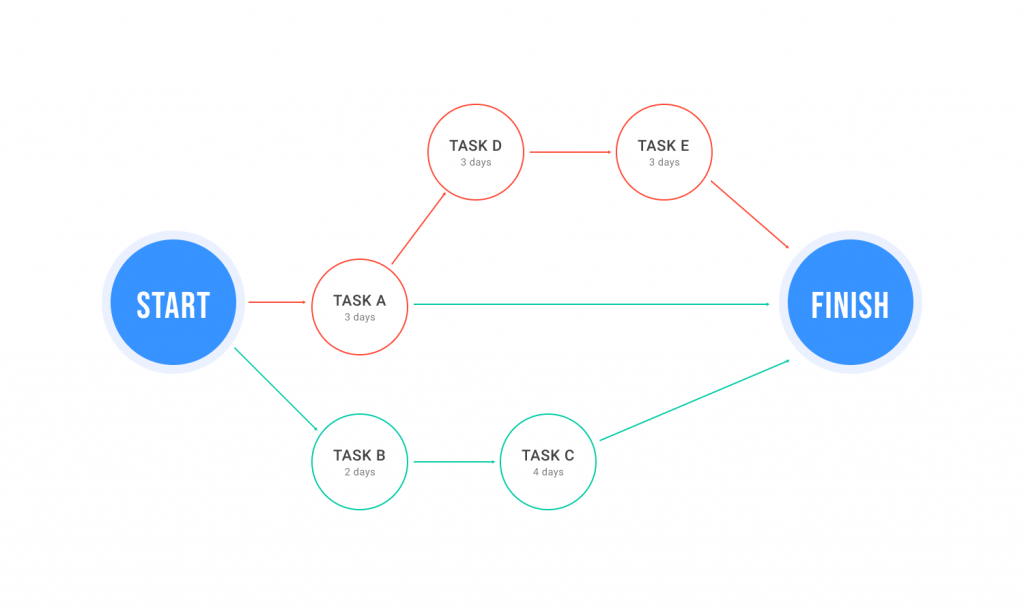
A critical path imitates events and activities in a project, presenting them in an interconnected network. Activities are rendered as “nodes,” and the beginning and end of the activities look like arches and lines between nodes.
The example of CPM using
Let’s consider the simplest example of applying critical path technology to a project with short deadlines. Imagine that our goal is to organize a parking lot on an empty asphalted area near the office. You need to act the following to do it:
- Choose a location.
- Clean the area from trash.
- Buy paint for marking.
- Measure the pad for a certain number of cars.
- Mark and paint all the parking elements.
- Install the gate.
It looks obvious – some stages of this project cannot begin until the others are finished. They are dependent. Steps 4,5,6 are sequential actions because they must occur in a certain order. In this example, these stages are the most important critical tasks for solving the problem. You will place them on the critical path of the project because you cannot start any stages until the others are completed.
Based on this plan, you can determine the duration of each stage and the entire project:
- 15 minutes to choose a place
- 90 minutes to clear the area
- 30 minutes to buy paint
- 45 minutes for measuring the area
- 60 minutes for marking
- 60 minutes to install the gate
How to build a critical path diagram?
You can use graphs, sections, columns, and arrows in a graphic scheme of your critical path to obtain the complete picture of the project and individual tasks.
It’s easy to visualize activities and dependencies on paper and use special programs and tools for these purposes. The simplest calculation of the critical path can be performed even in Excel using Gantt charts.

Key stages of Critical Path Method
CPM involves 6 consecutive steps:
- Identify activities /tasks
Knowing the scope of the project, you can divide the work structure into the list of activities, giving them names or codes. All activities in the project must have a duration and a specific date.
- Identify the sequences.
This is the most important step because it gives a clear idea of the links between activities and helps establish dependencies because some actions will depend on the completion of others.
- Create a network of your activities.
Once you have determined which actions depend on each other, you can create a network diagram or a path analysis chart. Using the arrows, you can easily connect activities based on their dependencies.
- Determine the time intervals for completing each activity.
Estimating how much time will be spent for each action, you will be able to determine the time needed to complete the entire project (small projects can be assessed in a few days; more complex ones require a long evaluation).
- Find a critical path.
The activity network will help you create the longest sequence on the path or the critical path using the following parameters:
- Early Start – the time when all previous tasks are completed.
- Early Finish – the nearest start time and the time required to complete the task.
- Late Finish – all activities are completed without postponing the deadlines.
- Late Start – the last end time minus the time it takes to complete the task.
How does the limitation of resources affect the method?
Careful resource management does matter. Trying to maximize the benefits of the critical path method and ensure the continuous development of projects, we can still face some limitations that can affect projects and create new dependencies. For example, if the team is suddenly reduced from 10 to 5 members, it means that you are faced the limitation of resources.
So the critical path turns into a “critical path of resources,” where the resources associated with each activity become an integral part of the process.
This means that some tasks must be performed in a different order, which can lead to delays and, therefore, make the project longer than expected.
As a conclusion
Although today the critical path method is often criticized, its background is still popular among project managers.
CPM has several advantages:
- Prioritizes tasks.
- Provides a clear understanding of project time intervals. This helps to reduce the time required to complete the project.
- Allows you to compare the planned and the actual progress.
- Assesses the risks.
- Helps in team members’ distribution.
- Helps the team stay focused on the main thing.
Using CPM, you can transfer less important tasks and focus your efforts on optimizing your work.
What do you think about the Critical Path Method? Have you applied it to your projects? Please, leave your comments if you have some bright examples.