How to Choose the Best Approach Among Different Project Management Methodologies?

The large family of management methodologies consists of many different members like any other large family. Some of them are distinguished by traditional views and approaches, some have very narrow interests and cannot get along with everyone, and some are considered very flexible and open to changes.
Each project is a separate unique life. This cannot be standardized. However, the processes that manage these projects are standardized according to the management methodologies.
If you manage the construction of a large bridge over the Thames – you will choose one tool, if your friend manages complex logistical processes between countries and continents, it will be more comfortable for his team to work with another method. Finally, the friend of your friend is a software developer, so there is a third methodology right for him.
In this article, we collect the most frequently used methodologies and highlight their advantages. So here we go!
Traditional Methodologies
Waterfall
One of the most common ways to plan projects is to arrange the sequence of tasks. It leads to a final deliverable and order.
This is what Waterfall offers. The traditional methodology seems to be one of the clearest for managing projects. This is how it works: your task must be completed before the next task begins in a connected sequence of items.
The approach is used for the projects that are resulted in physical objects.
Why project managers choose Waterfall?
There should be no doubt to use the traditional method if there is a clear understanding of how the final product should look like, if clients will not have access to change the project’s scope and if there will be no ambiguous requirements.
Waterfall includes 6 phases:
- Requirements
- Analysis
- Design and construction
- Testing
- Installation/ deployment
- Support and maintenance
Critical Path Method (CPM)
According to the concept, created in the 1950s, there are some tasks you can’t start until the previous task has been finished.
When these dependent tasks are string together from start to finish, you define a critical path.
What is it for? Defining a critical path assists in prioritizing and allocating resources to get the most important work done. It also helps to reschedule lower priority tasks.
Agile Methodologies
Agile members in the family of PM methodologies are based on iterative development.
This type of development implies that solutions evolve through collaboration between cross-functional teams. There are no specific recommendations and the model outlines the principles that use flexible methods.
The term was created in the USA in 2001 by 17 developers who were discussing their ideas and software approaches within the meeting. They collected the main values and principles in the Manifesto for Agile Software Development.
Agile development presumes 6 essential stages:
- Plan. When you’ve determined the idea, the project team should define and plan the main features.
- Requirements analysis. At this stage, you should arrange meetings with managers and users to identify business goals and needs and note the essential issues. Do not forget about SMART goals.
- Design. The whole picture of how the product will look like.
- Implementation. Coding, development and first testing of the features.
- Testing. To make sure your product solves customer needs and matches user stories.
- Deployment. The final stage of delivering the product to your clients after all tests.
Agile Project Manager should be responsible for the important issues:
- To maintain all values and practices in the project team.
- To remove any borders and difficulties.
- To hold and moderate all meetings.
- To enhance the practices used in the development process.
- To motivate the team.
Nowadays Agile methodology can refer to the popular frameworks. These frameworks are Scrum, Kanban, Extreme Programming, Adaptive Project Framework and Crystal Clear.
All of them have something in common. Project tasks are made clear by customers while the final deliverable can change. All frameworks assume iterative cycles for project teams, and the continuous collaboration is the key thing within the project team and with project stakeholders.
Scrum
As the most popular Agile framework, Scrum demonstrates the essential Agile model features best of all. Scrum sprints last 1-2 weeks and allow to deliver software on a regular basis. This is the main but not the only thing that highlights the differences between Scrum and Kanban.
According to the framework, Scrum PM shares responsibilities among a product owner, Scrum Master and the team.
- A Product owner is responsible for all business issues of the project. He/she makes decisions about the product and balances all priorities.
- A Scrum Master helps team members to get the most effective results and act together. Removing impediments, tracking progress, facilitating discussions and arranging meetings are also the fields of Scrum Master responsibilities.
- A team manages the determining how to achieve the product’s goals. The members choose the appropriate technical practices.
Kanban
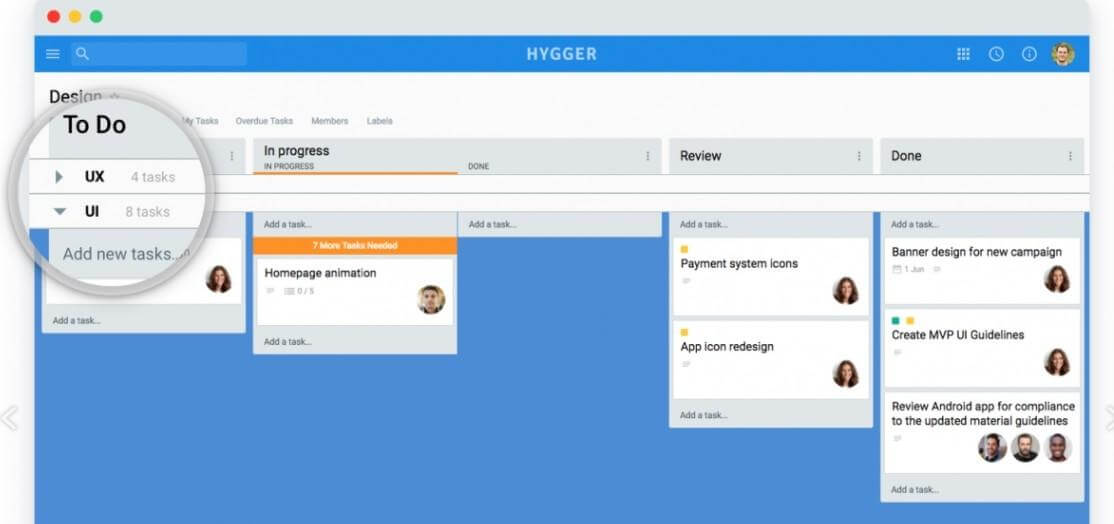
A visual card or a billboard is the translation of Kanban from Japanese. Kanban is a visual framework for Agile implementing with great benefits for software development. It promotes small and continuous changes to a project’s system. Kanban is widely used by developers to support a production system and the way to promote improvement.
The approach is appropriate for work that requires steady output. Project managers and team members use visual representations of their tasks often with the help of sticky notes or using smart services such as Hygger. They move the tasks through predetermined stages to see progress and possible roadblocks.
Kanban boards with smart columns and cards are also the great solution for product managers to maintain product backlog.
Extreme Programming
Extreme Programming (XP) is another Agile method of software development that is intended to improve quality for evolving customer needs.
XP, as well as the original Agile concept, includes short sprints, frequent iterations, and constant collaboration with stakeholders.
The methodology got its name because the elements of traditional development practices are taken to “extreme” level.
Adaptive Project Framework
Adaptive Project Framework (APF) was created on the basis of the view that most projects cannot be managed using traditional PM methods, due to changing and uncertain requirements.
The method begins with a Requirements Breakdown Structure to define project goals based on product requirements and features.
Then the project has iterative stages. Teams evaluate previous results to improve performance and practices at the end of each stage. Stakeholders can also change the project’s scope at the start of each stage.
Crystal Clear
Crystal Clear is another way to implement Agile methodology. The approach can be used by teams of 6- 8 developers. The method is basically focused on people, not processes.
Crystal Clear method has its 7 properties: the first 3 are compulsory and the others are optional. Here they are:
- Frequent Delivery
- Reflective Improvement
- Osmotic Communication
- Personal Safety
- Focus
- Easy Access to Expert Users
- Technical Environment with Automated Tests, Configuration Management & Frequent Integration.
The Process-based Methodologies
These members of the project management methods family are connected with business process management where each methodology focuses on work as a collection of processes.
Someone does not include them in the PM methods’ list but anyhow they are worth to be considered as the valid ways execute a project plan:
- Lean is focused on streamlining and cutting out waste.
First, managers need to create a work process breakdown to define and eliminate delays and bottlenecks. The main idea is to do more with less. For example, to deliver value to a client using less money, time and manpower.
- Six Sigma is a method that is aimed to improve the quality of a process by measuring the defects or bugs and getting them down.
- Lean Six Sigma – as the combination of the minimalist approach of Lean and the quality improvement of Six Sigma, this method focuses on eliminating waste so that projects are more cost-effective, efficient and totally answer clients’ needs.
Other PM Methodologies
The PMI/PMBOK Methodology
Some people will argue that this method should be included in the list of PM techniques. Project managers who live in an ideal insist that this method is just the set of standards and conventions for managing projects.
But they will definitely receive a counterargument from those project managers who use PMI in their companies.
The approach helps to break down projects into the five process:
- initiating
- planning
- executing
- controlling
- closing
This structure was agreed by the Project Management Institute (PMI) and also documented in the Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK).
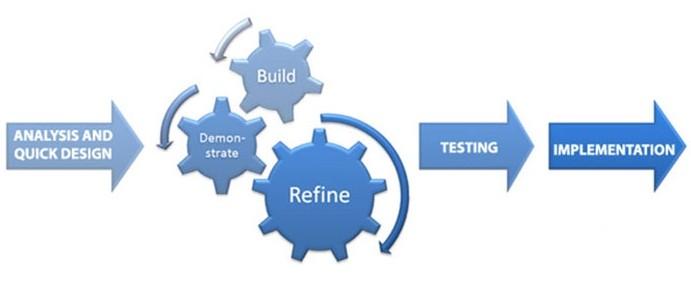
Rapid Application Development (RAD) methodology
RAD is a management methodology, most commonly used in software development projects. The main goal here is to quickly and efficiently create an app and follow 4 stages:
- Planning
- Custom Design
- Fast construction
- Switching
This method helps to improve the project’s performance indicators and increase the quality of risk management.
However, RAD is not so good for large-scale projects in IT industry because it can lead to poor code quality and requires permanent client’s involvement.
How to choose the right project management methodology?
So how to select the best one from the methods’ profusion?
Do not panic, just weight all the pros and cons. Clarify your project requirements, goals and objectives. Think about your final deliverable and the benefits.
Waterfall will be good for a physical object with definite materials and clear stakeholder expectations, any Agile method will help to manage an app that is not stable yet, and so on.
If you’ve made your choice, your next goal is to prepare the team for collaboration. In any case, be sure that there is no product or project for which a suitable methodology wouldn’t be found.