Team Roles in Agile Methodology

Every project management methodology has a particular structure of teams. Usually, it depends on the software development practices that are typical for a certain method. The structure of the team defines the roles and responsibilities of its members. In this article, we will tell you about the roles that are typical for Agile methodology. But before doing that it is necessary to give the full definition of this method and describe its main features.
Agile is a popular approach to software development that originated in the early 2000s when a group of experienced programmers decided to create a methodology that is suitable for modern complex projects. Agile was invented in response to the traditional waterfall methodology. Waterfall was the only software development method for many years. However, it was not perfect. The structure of Waterfall projects was sequential, so Waterfall developers had to run them from the very beginning any time when they detected bugs in the initial parts of the code. The structure of Waterfall teams was also very inconvenient. It was strict and hierarchic, so such teams could not act fast. In Agile things are different.
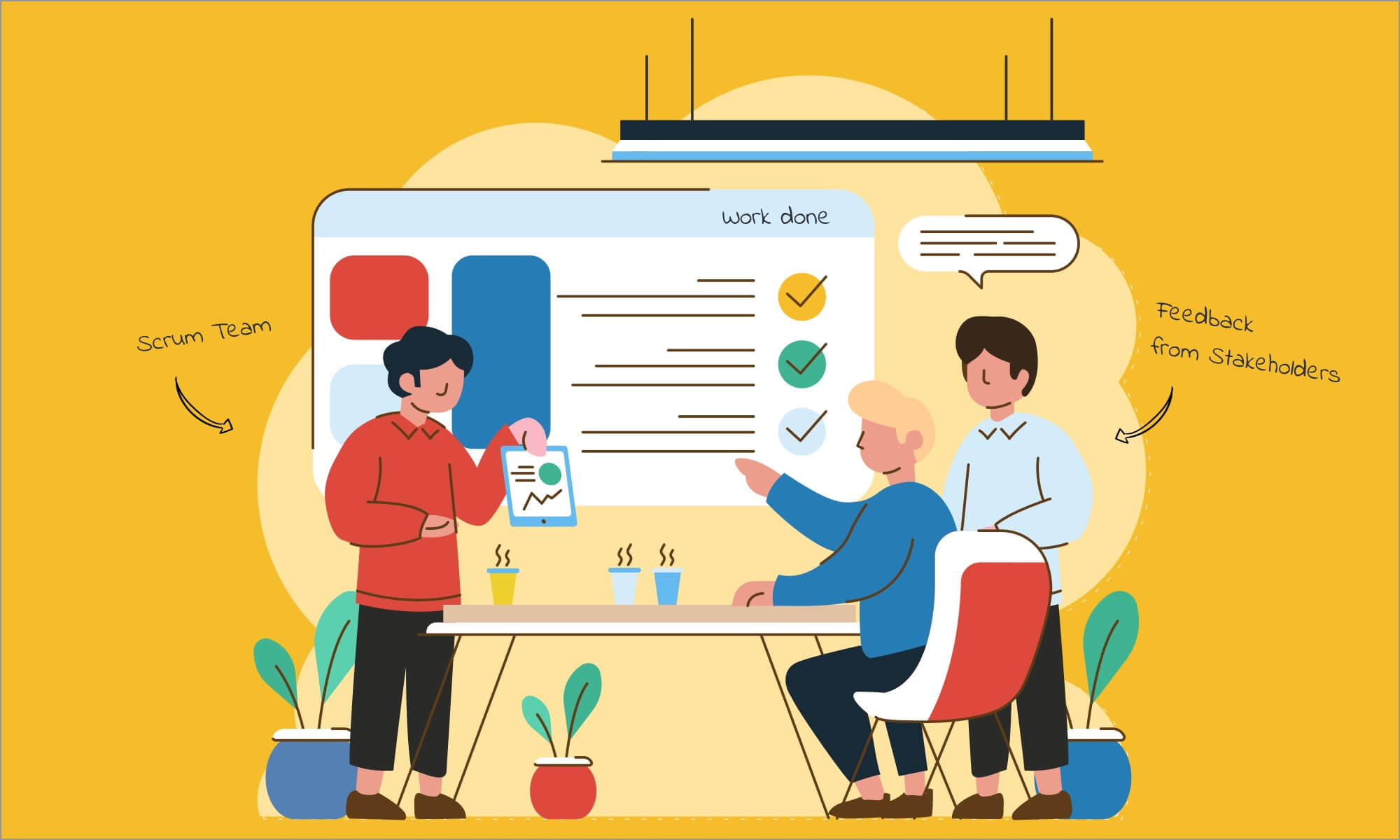
The methodology is based on three main principles: strong communication between the team members, high degree of customer involvement, and iterative structure of projects. Strong communication is required because Agile teams are small and self-managing. It means that their members have to communicate constantly to perform their tasks successfully. The degree of customer involvement in Agile projects is high because the client is the only person who has expectations regarding the final product.
Cases when the customers change their requirements to the future software product during the period of project realization are not rare. That is why Agile developers, unlike their colleagues who work in Waterfall, prefer to contact the customer during all period of project realization. Such an approach allows them to achieve extremely high user acceptance of final products. Iterative cycles are required to make the process of software development flexible. In the traditional Waterfall methodology, it is impossible to change the plan of the project while it is implemented. In Agile everything is possible. The intermediate products are introduced to the clients after each iterative cycle, so they can estimate them. The team can make amendments to the project’s plan based on the result of such estimation.
Now, as we know what Agile is, let’s describe the typical roles of Agile teams.
As already mentioned above, Agile teams are small and self-managing. Usually, they include less than 15 people. That is why they have no roles typical for the traditional software development methodology like testers, analysts, and project managers. Agile teams are responsible for the results of their work as a whole. However, some Agile methodologies like Kanban and XP can include the above-mentioned roles if it is necessary to deliver their products faster.