Kanban vs Traditional Method

Most developers agree that it is quite hard to compare various software development methodologies because they were designed for different types of projects. However, there are still programmers out there who want to know what methodology is better. Additionally, it is sometimes necessary to compare software development methods to define the difference between them and understand them better. In this article we will compare Kanban with the traditional method of software development.
Kanban originated in Japan in the 1940s. Initially it was a methodology for manufacturing. At that time a famous Japanese corporation Toyota had large problems with product delivery, so its managers have decided to invent a methodology to improve the manufacturing process. Initially Kanban was based on three main principles: workflow visualization, limitation of work in progress, and iterative structure of project realization. These Kanban principles were applied to software development at the beginning of the 2000s. Today Kanban is considered one of the most popular Agile methodologies.
Like in other Agile methods, its projects have iterative structure. However, Kanban has no separate plans and does not formulate separate task backlogs for its iterative cycles. A Kanban iteration is a lifecycle of a certain task. It is a period required to perform it and add new functionality to the software product.
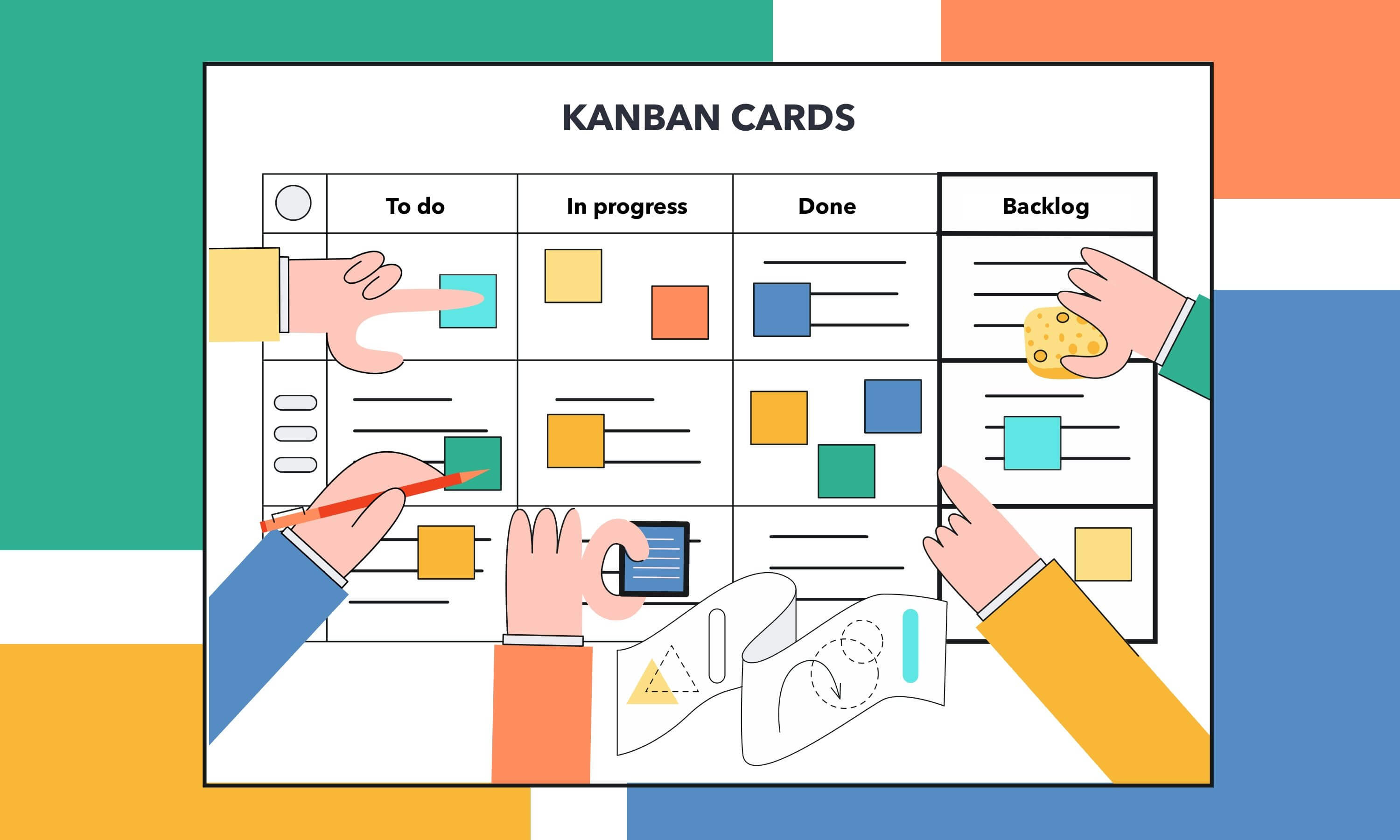
The workflow of Kanban teams is usually visualized on Kanban boards. These devices are tables with several columns. Each column depicts a certain stage of task performance. When the task passes this stage, it moves to the next column. Such visualization is required to see the progress of the entire project and certain tasks.
Limitation of work in progress is very important to organize the effective work of Kanban teams. Kanban teams always limit the amount of tasks they are performing at a certain moment. Usually they work on two tasks at the same time. After one of these tasks is finished, the team begins its work on the next task. The order of task performance can be changed by the customer any moment.
In traditional Waterfall methodology things are different. The method originated in the 1950s with the software development industry itself. It was, actually, a typical hardware development methodology applied to software engineering. Today Waterfall is the most popular software development method in the world. Like Kanban it is based on three principles. But these principles are different. They include: low degree of customer involvement, strong documentation, and sequential structure of projects.
The degree of customer involvement in Waterfall projects is very low. Waterfall teams conduct only two meetings with their clients during every project.
Strong documentation is required because of the low customer involvement. Waterfall developers begin the process of documentation formulation at the first meeting with their client.
The structure of Waterfall projects is sequential, unlike the structure of Kanban projects.